Heart Surgery in Taiwan
Search and Compare the Best Clinics and Doctors at the Lowest Prices for Heart Surgery in Taiwan

Find the best clinics for Heart Surgery in Taiwan
No clinics available
Turkey offers the best prices Worldwide
Price: $ 4,000

- Home
- Taiwan
WHY US?
At Medijump, we're making medical easy. You can search, compare, discuss, and book your medical all in one place. We open the door to the best medical providers worldwide, saving you time and energy along the way, and it's all for FREE, no hidden fees, and no price markups guaranteed. So what are you waiting for?

Free

Best Price

Widest Selection

Risk-Free
What you need to know about Heart Surgery in Taiwan
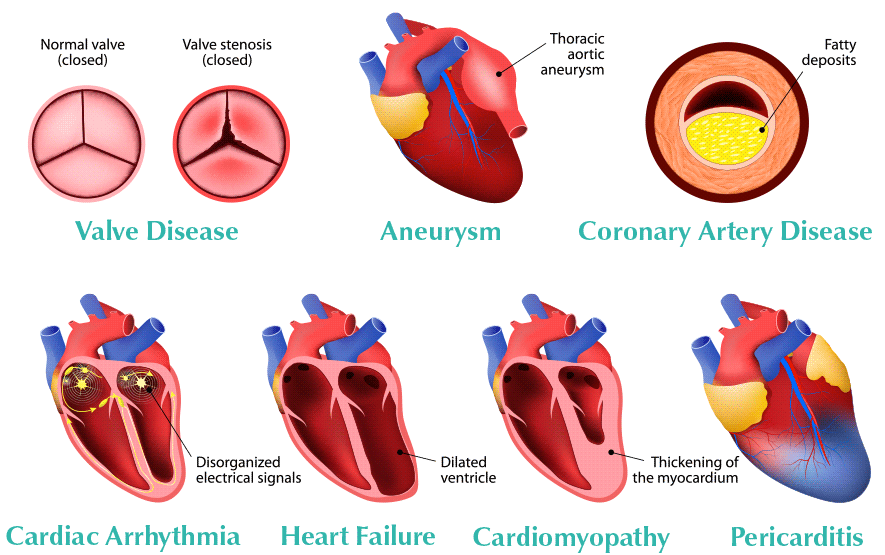
Heart surgery is any type of surgery performed to correct problems with the heart if other treatments cannot be used or have not worked. It can be done for both children and adults. Numerous problems can be addressed with heart surgery, including amyloidosis, arrhythmia, cardiomyopathy, aortic disease, coronary artery disease, heart failure, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, congenital heart disease, vulvar heart disease, and pericarditis.
Your doctor may use heart surgery to:
-
Replace or repair heart valves that don't work well
-
Treat heart failure and coronary heart disease (CHD)
-
Place medical devices to help support heart function
-
Control abnormal heart rhythms
-
Replace a damaged heart with a healthy one from a donor.
What is the cost of a Heart Surgery in Taiwan?
The price range for a Heart Surgery in Taiwan may fluctuate widely, influenced by various elements. These encompass the intricacy of the operation, the health status of the individual, and the surgeon's expertise level. Other correlated charges consist of preliminary screenings and examinations, anesthesia, post-surgery care, rehabilitation, and follow-up consultations. The monetary aspect is a pivotal consideration, and comprehending medical insurance coverage plus potential personal expenses is crucial.
Economic efficiency goes beyond just considering the immediate cost. One must also take into account the enduring health advantages, the decline in the continuous medication expenditures, the enhancement in life quality, and the potential for an extended lifespan. These considerations play a significant role when evaluating the overall financial consequences of the procedure.
What are the types of Heart Surgery?
There are various types of heart surgery. The following are some of the most common types:
1. Coronary artery bypass graft (CABG)
This surgery is usually used to treat patients with severe coronary heart disease (CHD). It can improve the blood flow to your heart. In CABG, a healthy vein or artery from another area of your body is taken and connected to the blocked coronary artery to supply blood. The grafted vein or artery goes around (bypasses) the blocked part of the artery, making a new path for your blood to flow to the heart muscle. During one surgery, surgeons can bypass multiple blocked coronary arteries.
2. Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) or coronary angioplasty
PCI is another treatment for CHD. It involves the insertion of a thin, flexible tube with a balloon at its end through a blood vessel to the blocked or narrowed coronary artery. Once the tube is in place, your surgeon inflates the balloon to push the plaque against the artery wall or to widen the narrowed artery. This is done to restore blood flow. A stent may also be placed to help keep the artery open.
3. Heart valve repair or replacement
Heart valve repair or replacement is used to treat damaged or diseased valves, or when your heart valves do not work the way they should. Your surgeon can either repair the valve or replace it with man-made or biological valves. Biological valves are made from cow, pig, or human heart tissue and may also have man-made parts.
One way to repair the valve is by inserting a catheter with a small balloon at the tip through a large blood vessel. The catheter is then guided to the heart and the balloon is inflated and deflated to widen a narrow valve.
A heart transplant is mostly performed on patients with end-stage heart failure. This surgery involves:
- Removing a patient’s disease heart and replacing it with a healthy one from a deceased donor.
- Insertion of a pacemaker or an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD)
- Insertion of a pacemaker or ICD is used to treat arrhythmia when medication does not work.
A pacemaker is a tiny device placed under the skin of your chest or abdomen. The device is connected to your heart chambers through wires. It can control your heart rhythm using low-energy electrical pulses. An ICD is similar to a pacemaker. It is a small device placed under the skin of your abdomen or chest and is connected to your heart through wires. It is used to check your heartbeat for dangerous arrhythmias by sending an electric shock to your heart, which will restore your heart rhythm to normal.
5. Maze surgery
This is another treatment for arrhythmia. This surgery involves creating a pattern of heart tissue inside the upper chambers of the heart to transmit electrical signals along a controlled path to the lower heart chambers.
6. Aneurysm repair
Aneurysm repair involves replacing a weak section of the heart or artery with a graft or patch. This is done to repair a balloon-like bulge within the wall of the heart muscle or the artery.
7. Surgery to place Ventricular Assist Devices (VAD) or Total Artificial Hearts (TAH)
If you have heart failure that is not responding for treatment or if you are waiting for a heart transplant. Your doctor may recommend VAD insertion. A VAD is a mechanical pump that can support the function of your heart and your blood flow if you have a weak heart. If both of your ventricles do not work well due to end-stage heart failure, TAH may be used. A TAH is a device used to replace the ventricles (the two lower chambers of the heart).
8. Transmyocardial Laser Revascularization (TMR)
TMR is used to treat angina when other treatments do not work. It involves creating small channels through the muscle of the heart into the lower left chamber of the heart using lasers.
What does the Procedure Involve?
Different surgical approaches can be used to perform the types of heart surgery mentioned above. The surgical approach depends on your specific problem, general health, and other factors. Below are the surgical approaches to perform heart surgery:
-
Open heart surgery is any kind of surgery in which a surgeon creates a large cut in the chest to open the rib cage to expose the heart and operate on it. In some cases, the surgeon may also open the heart. With this surgical approach, your heart is not beating. Instead, it is connected to a heart-lung bypass machine that takes over the heart’s pumping action.
-
Off-pump heart surgery is usually used to do CABG. It is similar to open-heart surgery, but your heart is not stopped and a heart-lung bypass machine is not used.
-
Minimally invasive heart surgery involves creating small incisions in the side of your chest between the ribs. It may or may not use a heart-lung bypass machine. The incisions are created to insert small tools. In some cases, thin robotic arms may also be used to help your surgeon (robotic-assisted surgery).
How Long Should I Stay in Taiwan?
A number of variables, including the patient's health, the complexity of the surgical procedure, and their rate of recovery, can greatly affect how long a patient stays for a Heart Surgery. You will likely have to stay in the hospital for several days after heart surgery. It is recommended that you stay in Taiwan for at least 10 to 14 days for initial recovery and follow-up checkups. This time frame also paves the way for the start of the physical recovery program and offers a chance for any needful alterations to medication.
What's the Recovery Time?
The recuperation duration, a vital part of the Heart Surgery, can alter based on factors like the patient's age, overall health, and the kind of operation they underwent. The time to heal can differ, contingent on the nature of your cardiac operation and the surgical method employed. Your medical practitioner will inform you when you can recommence your routine activities. Complete recovery may necessitate anywhere from 6 to 12 weeks or even longer. Typically, open-heart procedures necessitate an extended recuperation duration.
Throughout this healing phase, it's suggested for patients to slowly augment their physical exertion while simultaneously adhering to a cardiac-friendly diet. It's absolutely imperative for patients to show up for frequent follow-up check-ups to track their progress, tweak medications if required, and to immediately address any possible issues or complications.
What About Aftercare?
Post-Heart Surgery follow-ups are vital for a successful recovery process. Frequently, it means embarking on lifestyle modifications like adherence to a nutritious diet, continuous engagement in physical exercise, refraining from smoking, moderation in alcohol consumption, and mastering stress management. Routine check-ups are essential to verify proper patient healing and to make necessary medication alterations.
Physiotherapy may also be advantageous since it can enhance strength and boost cardiovascular health. Implementing calming practices such as yoga or meditation can aid in stress management while bolstering mental wellness. Moreover, understanding the symptoms of possible complications such as infections or cardiovascular complications is crucial for patients, and they should strive for immediate medical attention if these symptoms emerge.
Ongoing care is often needed, these include regular checkups with your doctor (you may do these checkups with your local doctor at home or your doctor in Taiwan), cardiac rehabilitation, and healthy lifestyle changes.
What's the Success Rate?
The effectiveness of a Heart Surgery within Taiwan commonly relies on multiple factors, such as the patient's health prior to the surgery, the nature and intricacy of the cardiac ailment, and the surgeon's skill level. It is crucial to understand that success is gauged not merely by the immediate results post-procedure, but also by long-term survival, enhancement of life quality, and alleviation of symptoms.
Heart surgeries frequently yield outstanding outcomes and are generally considered safe. Patients need to bear in mind that the procedure is typically part of a comprehensive treatment strategy. Ongoing medication, a balanced diet, consistent physical activity, and lifestyle changes are all fundamental to maintaining the long-term benefits and success of the surgery. Regular health screenings and discussions with your physician are also critical to monitor improvement and identify any potential issues early on.
Are there Alternatives to Heart Surgery?
Heart surgery is not always necessary to treat heart-related problems. In some cases, your doctor may recommend medications or nonsurgical procedures to address the problem. For instance, to prevent abnormal electrical signals from moving through your heart, your surgeon may use a procedure called catheter ablation. Each alternative comes with its own set of benefits and risks - it's crucial to discuss these with a healthcare professional.
What Should You Expect Before and After the Procedure
Prior to the Heart Surgery, it is advised for patients to have an in-depth discussion with their healthcare provider concerning the operation, its advantages, potential risks, and recovery timeframe. Tests such as blood work, chest radiographs, and electrocardiograms may be deemed necessary before the surgery. Patients must divulge their entire medical history and provide a list of medications they are currently taking. Understanding post-surgery care requirements and necessary adjustments to lifestyle is also vital.
After the Heart Surgery, patients should anticipate spending a few days in the critical care unit and a week or more at the [clinic](https://www.mymeditravel.com/). During the recovery lifespan, a slow augmentation in physical activity is advised, however, harsh activities and heavy lifting should be avoided. Regular checkups, medication modifications, and potential lifestyle alterations form part of the aftercare program. The recovery phase following the Heart Surgery may demand time and patience, however, the end result can be a significantly enhanced quality of life.
What are Potential Risks of Heart Surgery?
Like any major surgery, Heart Surgery also carries potential risks. These can include complications like:
- Infection and bleeding
- Irregular heart rhythm
- Memory loss or cognitive issues
- Heart attack or stroke (in rare cases)
- Reactions to anesthesia.
The risk of complications is generally higher if heart surgery is performed in an emergency situation, such as during a heart attack. It is also higher if the patient has other diseases, such as diabetes.
Whilst the information presented here has been accurately sourced and verified by a medical professional for its accuracy, it is still advised to consult with your doctor before pursuing a medical treatment at one of the listed medical providers
No Time?
Tell us what you're looking for and we'll reachout to the top clinics all at once
Enquire Now

Popular Procedures in Taiwan
Prices Start From $2,000

Prices Start From $300

Prices Start From $1

Prices Start From $911

Recommended Medical Centers in Taiwan for procedures similar to Heart Surgery

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available
- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available
Heart Surgery in and around Taiwan
About Taiwan
Whilst still a part of the Republic of China, the small island of Taiwan maintains a wealth of ancient Chinese culture and traditions mixed with modern-day Western inspirations. With its food-loving locals and award-winning whiskeys, Taiwan is a land of surprises. With 14 JCI accredited facilities in Taiwan, Taipei, the capital, is home to most, many of which are part of the University Hospitals and offer a range of specialist tertiary care. The country welcomes an ever-increasing number of medical tourists each year, many of which travel for Heart Surgery procedures. Medical Tourists mostly travel from the mainland or from within the region.
Popular parts of Taiwan
Taiwan is one of the most densely populated countries in the world with 23.5 million inhabitants. The country has amazed tourists with its dynamic cities, vibrant culture, interesting history, and incredible natural scenery.
- Taipei is the capital of Taiwan. It is the financial, political, and cultural center of the country. The city is influenced by Chinese culture as well as Japanese, Southeast Asian, and American. There are many things to enjoy in this city, such as delicious food in Rahoe Night Market, enjoy a bird’s eye view of Taipei from Taipei 101 Observatory, visit the incredible Chiang Kai-shek Memorial Hall, and be inspired by the city’s many museums.
- Kaohsiung is Taiwan’s largest port. It’s an urban city that embraces its cultural venues. The most popular tourist destination is the Lotus Pond, a beautiful artificial lake filled with lotus plants and surrounded by temples. Tourists can also visit Pier-2 Art Center, see the Dome of Light, explore Cijin Island, or visit the Fo Guang Shan Monastery.
- Tainan, as the oldest city in Taiwan, has a fascinating culture and history. For historical sights, tourists can visit the Anping Fort, Anping Tree House, or learn Taiwanese embroidery. The city is now filled with quaint cafes tucked within the alleys.
- Hualien has breathtaking natural beauty. It’s the perfect place for tourists who want to get away from busy cosmopolitan cities. Visit the Eternal Spring Shrine, check out the popular Taroko Gorge, fall in love with Qingshui Cliffs, hike the Shakadang trail, and eat the amazing food.
- Taichung is a lively city located in the west-central part of the island. Taichung offers many unique things to see and do. National Taichung Theater will leave tourists in awe by its beautiful architecture. National Taiwan Museum of Fine Arts, Rainbow Village, Gomei Wetlands, Miyahara, and Fengjia Night Market are among the most popular tourist attractions.
Weather and Climate in Taiwan
- Spring starts in March and lasts until May. The average temperature is between 18°C and 24°C. Early rain showers and thunderstorms begin in this season. Heavy rainfall hit the island around mid-May.
- Summer can get extremely hot and humid with an average temperature of 27°C to 30°C. The season starts from June to August. Summer is also the wet season and typhoons are a real possibility especially in July and August. This is the peak season for tourism.
- Autumn has pleasant weather conditions. The rains decrease and the heat will drop. The season starts from September to November with an average temperature of 21°C to 27°C.
- Wintertime is from December to February and it is the coolest and driest season of the country. The average temperature drops to 16°C - 18°C.
Getting Around in Taiwan
Taiwan Taoyuan International Airport is the main airport in the country, located about 40km west of Taipei in the Dayuan District, Taoyuan. It is the hub for 6 airlines including two of Taiwan’s major airlines, China Airlines, and EVA Air. It has international connections with almost every country in the world. The airport serves major airlines as well as budget airlines such as Air Asia, Eastar Jet, Air Busan, and Tiger air Taiwan. There are other airports that serve international and domestic flights such as Taichung Airport, Tainan Airport, Siaogang Airport, and Taipei Songshan Airport.
Tourists arriving at Taiwan Taoyuan International Airport have a variety of transport options such as buses, taxis, car rentals, and Taoyuan Airport MRT. Buses are the cheapest option to get to the city center. Tourists who head towards the Taipei 101 area should take Bus no. 1960, while bus no. 1819 and 1961 will take tourists near Taipei Main Train Station.
Taxis are available in Terminal 1 and Terminal 2’ arrivals lobby. The fare is based on a meter and will usually cost around 1,200 TWD (40.50 USD). A journey to the city center takes about 50 minutes and taxis operate for 24 hours.
Taoyuan Airport MRT is the fastest way to reach Taipei’s city center. It will take tourists to Taipei Main Station in 35 minutes and costs 160 TWD (5.40 USD). The MRT operates from 6.05 am to 11.35 pm.
Tourists can travel around Taiwan by normal train (TRA). It is an affordable option; a train ride from Taipei to Kaohsiung costs around 845 TWD. Tourists who need a quicker travel time can opt for Taiwan High-Speed Train (HSR). The train travels from Taipei to Kaohsiung in just 90 minutes.
The cheapest way to travel around Taiwan is by bus. Buses are readily available and will reach small villages and mountain resorts. The country provides Taiwan Tourist Shuttle bus system that offers 42 routes to more than 100 tourist destinations.
Taxis and MRT is the best way to travel around big cities. In Kaohsiung, getting around in a bicycle is the best way to explore as it is one of the most bicycle-friendly cities in Taiwan.
Tourist Visas in Taiwan
Citizens of 65 countries do not require a visa to visit Taiwan and can stay for up to 90 days. Nationals of Turkey can obtain a visa on arrival valid for 30 days. It is best to check to the nearest embassy or consulate for visa requirements. Since January 2016, Taiwan offers an eVisa program for 18 countries including Saudi Arabia, Peru, Oman, and United Arab Emirates.
Additional Information
- Local Currency: The local currency is the New Taiwanese Dollar (TWD). 1 USD converts to 31.98 TWD.
- Money & Payments: ATMs are widely available except in villages. They’re usually located in convenience stores and banks. Credit cards are accepted in hotels and top-end restaurants. Always carry cash because small stalls and night market joints only accept cash. Tipping is not mandatory but is still appreciated.
- Local Language: The national language is Hakka, Mandarin, Taiwanese Hokkien, Matsu, Formosan languages, and sign language. English is common, especially in the tourism area. English is spoken more in Taipei.
- Local Culture and Religion: Taiwan has diverse religious beliefs. Buddhism and Taoism are two of the biggest religion in the country followed by Christianity, Yiguandao, Tiandism, Miledadao, Zailiism, and Xuanyuanism.
- Public Holidays: Taiwan celebrates Chinese New Year for a week in February. The country hosts several festivals such as Lantern Festival in February, Dragon Boat Festival in June, and Mid-Autumn Festival in September.
Popular Searches
- Plastic Surgery in Thailand
- Dental Implants in Thailand
- Hair Transplant in Thailand
- Breast Augmentation Thailand
- Gastric Sleeve in Thailand
- Gender Reassignment Surgery in Thailand
- Laser Hair Removal in Bangkok
- Botox in Bangkok
- Dermatology in Bangkok
- Breast Augmentation in Bangkok
- Coolsculpting in Bangkok
- Veneers in Turkey
- Hair Transplant in Turkey
- Rhinoplasty in Turkey
- Stem Cell Therapy in Mexico
- Rhinoplasty in Mexico
- Liposuction in Mexico
- Coolsculpting in Tijuana
- Rhinoplasty in Korea
- Scar Removal in Korea
- Gastric Sleeve in Turkey
- Bone Marrow Transplant in India
- Invisalign in Malaysia
- Plastic Surgery in the Dominican Republic
- Tummy Tuck in the Dominican Republic
- Plastic and Cosmetic Surgery in Poland
- Rhinoplasty in Poland
- Hair Implant in Poland
- Dental Implants in Poland
- IVF in Turkey