Male Breast Cancer Treatment in Brazil
Search and Compare the Best Clinics and Doctors at the Lowest Prices for Male Breast Cancer Treatment in Brazil
Find the best clinics for Male Breast Cancer Treatment in Brazil
No clinics available

- Home
- Brazil
WHY US?
At Medijump, we're making medical easy. You can search, compare, discuss, and book your medical all in one place. We open the door to the best medical providers worldwide, saving you time and energy along the way, and it's all for FREE, no hidden fees, and no price markups guaranteed. So what are you waiting for?

Free

Best Price

Widest Selection

Risk-Free
What you need to know about Male Breast Cancer Treatment in Brazil
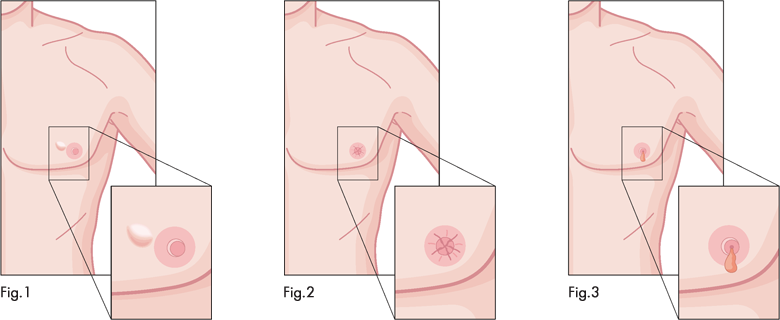
There are different types of treatment for men with breast cancer. Because there have been few clinical treatments for male breast cancer, most doctors recommend the treatment options based on their experience of treating women with breast cancer.
To determine your treatment options, several important factors need to be considered. These include the stage of your cancer, how fast the cancer is growing, your overall health, and your preference. The treatment for male breast cancer often involves surgery and may be combined with other treatments. The five types of treatment used are surgery, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, radiation therapy, and targeted therapy.
What does the Procedure Involve?
Surgery
Surgery is usually the first treatment if a breast abnormality is found to be cancerous. It aims to remove the tumor, as well as some surrounding breast tissue. There are several types of surgery that can be performed:
-
Mastectomy – The most common type of mastectomy performed in men is called a modified radical mastectomy. This surgery involves removing the nipple, areola (the dark, round area around the nipple), and all of the breast tissue. Many of the lymph nodes under the arm, and sometimes, part of the chest wall muscles may be removed as well.
-
Lumpectomy – Also known as breast-conserving surgery, lumpectomy is a procedure to remove cancer but not the breast itself. It involves removing the tumor (lump) and a small amount of normal tissue that surrounds it. However, this type of surgery is rarely done because men’s breasts are very small. By the time the tissue and the surrounding tumor have been removed, very little breast tissue is left.
-
Sentinel lymph node biopsy – this type of surgery involves removing a few lymph nodes for testing. The lymph nodes are most likely to be the first place that cancer cells would spread. Your doctor will remove a few lymph nodes and analyze them. If no cancer cells are found, then there is a good chance that breast cancer has not spread. However, if cancer is found, additional lymph nodes will need to be removed for further testing.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a type of treatment that uses drugs to stop the growth of cancer cells, either by stopping the cells from dividing or by killing them. Chemotherapy drugs can be administered through a vein in your arm (intravenously) or taken by mouth in the form of a pill. Sometimes, both methods can be used. This type of treatment may be carried out after surgery to lower the risk of your breast cancer coming back. In men with advanced breast cancer or those with cancer that has spread to other areas of the body, chemotherapy may be the main treatment option.
Hormone therapy
Some types of breast cancer rely on certain hormones to grow (hormone receptor). With hormone therapy, the effects of these hormones are blocked. As a result, the growth of the cancer is stopped.
Hormone therapy for male breast cancer usually involves medication called tamoxifen. In some cases, the removal of the testes reduces the amount of certain male hormones in your body. Men who have breast cancer should never take testosterone as it causes the cancer cells to grow.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy is a type of treatment that uses high-energy beams, such as X-rays and protons, to kill or stop cancer cells from growing. Radiation therapy has two types:
-
Internal radiation therapy uses a radioactive substance that is sealed in seeds, wires, needles, or catheters that are placed near or directly into cancer.
-
External radiation therapy involves the use of a machine outside of the body. This machine sends radiation toward cancer.
Targeted therapy
Some men have an excess of a protein (HER2) that can make cancer spread quickly. In this case, your doctor will use drugs or substances to identify and attack specific cancer cells without harming normal cells. The drug may also boost your immune system, which gives it more strength to fight cancer.
How Long Should I Stay in Brazil?
Your length of stay depends on the type of treatment you have. With surgery, you usually need to stay in the hospital for at least a day and stay in Brazil for about 7 to 10 days. For chemotherapy, hormone therapy, radiation therapy, and targeted therapy, your length of stay can vary depending on your treatment schedule or treatment plan. Your doctor and/or medical travel team will be able to advise you on this.
What's the Recovery Time?
The recovery time for surgery can take around 4 to 6 weeks, but you should be able to return to work in 2 to 3 weeks following the surgery. Side effects after chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, and targeted therapy generally reduce within a few weeks to several months.
What About Aftercare?
After any type of treatment, your doctor will give you detailed aftercare instructions, what you should and foods to avoid, exercise your plan and restrictions. It is important that you follow the instructions closely. Remember, you will require regular checkups with your doctor for the rest of your life.
What's the Success Rate?
Male breast cancer treatment is safe and effective. However, the success rate depends on the stage of cancer and how fast the cancer is growing. All types of treatment carry possible risk and side effects, such as infection, bleeding, hematoma, nausea, vomiting, hair loss, and heart problems.
Are there Alternatives to Male Breast Cancer Treatment?
There are currently no other alternatives to the treatments mentioned above. Some men with breast cancer take part in a clinical trial. A treatment clinical trial is a research study used to obtain information on new treatments or help to improve current treatments for patients with cancer.
What Should You Expect Before and After the Procedure
Before male breast cancer treatment, you may experience uncomfortable symptoms and your cancer is likely to spread to other parts of the body. After successful male breast cancer treatment, most of the symptoms should be gone. You may also be incomplete remission (no evidence of disease or NED).
Whilst the information presented here has been accurately sourced and verified by a medical professional for its accuracy, it is still advised to consult with your doctor before pursuing a medical treatment at one of the listed medical providers
No Time?
Tell us what you're looking for and we'll reachout to the top clinics all at once
Enquire Now

Popular Procedures in Brazil
Prices Start From $95

Prices Start From $53

Prices Start From $2

Prices Start From $692

Recommended Medical Centers in Brazil for procedures similar to Male Breast Cancer Treatment

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available
Male Breast Cancer Treatment in and around Brazil
About Brazil
Occupying the title of the largest country in South America, Brazil embraces a diverse population of over 209 million people. The nation is globally renowned for its passion for football (also referred to as soccer in some parts of the world) and their dynamic, flamboyant carnival traditions, boasting a vibrant mix of music, dance, and colorful attire.
In addition to its vivacious culture, Brazil is a sanctuary of spectacular natural beauty. The country nurtures some of the world's most stunning natural wonders, including the dramatic Iguacu Falls and the world's largest tropical rainforest, the Amazon Rainforest, teeming with diverse plant and animal species. One can't miss the landmark figurine of Christ the Redeemer in Rio de Janeiro that towers 98-feet high, becoming a symbol of Brazil's deep-rooted religious faith and an iconic sight that captures hearts worldwide.
Brazil offers more than 60 JCI-accredited facilities and is one of the leading destinations in the world for cosmetic surgery, with Male Breast Cancer Treatment procedures being especially popular. Doctors are often Western-trained and speak English on top of Portuguese and Spanish. Local accreditations include the Consortium of Brazilian Accreditation and the Brazilian Hospital Medical Quality Organization (ONA). Popular locations within Brazil include the capital Brasilia, Rio de Janeiro, Sao Paulo, and Curitiba.
Popular Parts of Brazil
- Rio de Janeiro is a combination of natural attractions and metropolis. It is known to be a party city that offers good times and an unforgettable experience. Lounge around in the world-famous beaches of Ipanema and Copacabana, sample Brazilian cuisine, hike the summit of Corcovado and see the high statue of Christ the Redeemer, dance in Rio Carnival, and see the spectacular views of Ipanema and Guanabara Bay from the Sugarloaf Mountain.
- São Paulo is the largest city in Brazil. It is a huge city that at first glance seems intimidating. It offers hundreds of museums, quirky urban art, delicious cuisine, lively nightlife, and intense cultural experience. Visit Avenida Paulista (Paulista Avenue), a street filled with shopping centers, parks, bars, restaurants, museums, theatres, and cultural spaces.
- Salvador is full of vibrant cultures. It is the heart of Brazil’s Afro-Brazilian community. The city’s charm lies in its pastel-colored neighborhood, centuries-old architecture, and freshly-cooked acarajé and completed with wild festivals and capoeira circles every night.
- Brasília is Brazil’s capital. It’s very modern with futuristic architecture that looks more like artworks than ordinary buildings. It’s a paradise for architecture buffs. Besides the architecture, the food and nightlife in this city is something that should not be missed.
- Manaus might be isolated in terms of location, but it’s actually a large city with a prospering industry and a rich culture. The city is also filled with natural beauty; green spaces, waterfalls, and ecological parks surround its colonial buildings. It is the gateway to the Amazon Rainforest.
Weather and Climate in Brazil
As a large country, the weather in Brazil varies from tropical in the north to temperate in the south. A large part of the country lies in the topics. Brazil is a year-round destination because it has a steady average annual temperature. The temperature rarely drops below 20 °C.
Winter in Brazil starts in May and ends in September. The weather remains tropical in the north with an average temperature ranging between 20 °C to 30 °C. In Rio de Janeiro, the temperature varies between 14 °C to 25 °C. However, the evenings usually feel a lot colder.
During this particular season, one can expect a fair amount of rainfall in Rio, leading to many wet and rain-soaked days. If you plan a visit at this time, it's wise to keep that in mind and prepare accordingly. In contrast, further inland, São Paulo experiences significantly cooler temperatures compared to Rio, reflecting the country's vast geographical expanse and diverse microclimates spread across its regions.
This temperature drop might require some warm clothing, especially during late evenings and nights. So, whether you wish to enjoy the rainy murmur in Rio or seek the cool retreat of São Paulo, there's something unique for every traveler in Brazil during this season.
The temperature in Rio rise between November and March, with the highest temperature of around 40 °C but with a thermal sensation of around 50 °C. The Rain rarely lasts long during these months. In the north of Brazil, the rainy season starts in December. March and May see the heaviest rainfall. It’s hot and humid with frequent rain throughout the year in the Amazon.
Getting Around in Brazil
The most popular international airports are Rio de Janeiro–Antonio Carlos Jobim International Airport (popularly known as Galeão International Airport) and São Paulo/Guarulhos–Governador André Franco Montoro International Airport. Both airports serve domestic and international flights to many cities around the globe. The airports mainly serve major airlines but there are budget airlines such as Norwegian Air UK. Tourists can take taxis, bus, train, or car rental from both airports to the city centers.
Brazil is really big, so there will be a lot of long-distance travel to get around the country. The easiest and fastest way to get from one city to another is by domestic flights. The only downside is that the tickets are very expensive. LATAM and GOL Airlines offer multi-trip tickets or air pass. The most economical option is to buy an air pass if you plan to visit a number of different cities.
Buses are popular in Brazil, servicing most areas of the country. The bus system is excellent and provides a comfortable and economical way of travel. Be aware that the distance can be really tiring and overwhelming; some trips can take over 40 hours. The buses are operated by hundreds of different private companies, but the price is standardized. The fare varies from 75 BRL to 240 BRL. There are luxurious buses too.
A good way to get around major cities like São Paulo and Rio is to use Brazil Metro (subway). The fares are around 3.50 BRL to 3.80 BRL. You can purchase rechargeable travel cards. The metro does not operate at night. Be sure to watch your belongings at all times when traveling on the metro.
Taxis run on a metered system, but if you travel a bit further out of town, you need to negotiate the price with the driver. It is best to phone for a taxi or pick one up at a taxi station and make sure to get into a licensed taxi. Ferries and other water travel are important in many parts of Brazil.
Tourist Visas in Brazil
Nationals of 72 countries and territories can enter and stay in Brazil for up to 90 days without a visa. In some cases, an identity document may be accepted instead of a passport. Citizens of other countries, including China and India, must apply for and obtain a visa before entering Brazil. It is recommended to contact the nearest Brazilian embassy or consulate for the most up-to-date visa information.
Brazil offers an electronic visa (e-Visa) for citizens of eligible countries. The e-Visa is valid for two years and allows multiple entries for stays of up to 90 days per year. Applicants can apply for the e-Visa online through the Brazilian government's website.
Additional Information
- Local Currency: The official currency is the Brazilian Real (BRL). 1 USD will get you approximately 5.04 BRL.
- Money & Payments: ATMs are widely available in Brazil and it is the easiest way of getting cash in big cities. ATMs in smaller towns usually don’t work for non-Brazilian cards. Credit cards (Visa and MasterCard) are accepted in numerous shops, restaurants, and hotels. It might be handy to always have cash with you, but always be extremely cautious. Tipping is optional for housekeepers, tip parking assistants 2 BRL, or more since they do not receive wages and depend on tips. Taxis do not expect tips. Restaurants usually include a 10% service charge in the bill.
- Local Language: The official language is Portuguese. English is not widely spoken, especially outside Rio and São Paulo.
- Local Culture and Religion: The largest religion in Brazil is Christianity with more than 60% of the population follows Roman Catholicism.
- Public Holidays: Brazil celebrates major Christian religious holidays as well as Independence Day and Civil Servants Day. Festa Junina, Parintins Folklore Festival, and Oktoberfest are three of the biggest annual festival in the country.
Popular Searches
- Plastic Surgery in Thailand
- Dental Implants in Thailand
- Hair Transplant in Thailand
- Breast Augmentation Thailand
- Gastric Sleeve in Thailand
- Gender Reassignment Surgery in Thailand
- Laser Hair Removal in Bangkok
- Botox in Bangkok
- Dermatology in Bangkok
- Breast Augmentation in Bangkok
- Coolsculpting in Bangkok
- Veneers in Turkey
- Hair Transplant in Turkey
- Rhinoplasty in Turkey
- Stem Cell Therapy in Mexico
- Rhinoplasty in Mexico
- Liposuction in Mexico
- Coolsculpting in Tijuana
- Rhinoplasty in Korea
- Scar Removal in Korea
- Gastric Sleeve in Turkey
- Bone Marrow Transplant in India
- Invisalign in Malaysia
- Plastic Surgery in the Dominican Republic
- Tummy Tuck in the Dominican Republic
- Plastic and Cosmetic Surgery in Poland
- Rhinoplasty in Poland
- Hair Implant in Poland
- Dental Implants in Poland
- IVF in Turkey