Stomach Cancer Surgery in Spain
Search and Compare the Best Clinics and Doctors at the Lowest Prices for Stomach Cancer Surgery in Spain

Find the best clinics for Stomach Cancer Surgery in Spain
No clinics available
Poland offers the best prices Worldwide
Price: $ 512

- Home
- Spain
WHY US?
At Medijump, we're making medical easy. You can search, compare, discuss, and book your medical all in one place. We open the door to the best medical providers worldwide, saving you time and energy along the way, and it's all for FREE, no hidden fees, and no price markups guaranteed. So what are you waiting for?

Free

Best Price

Widest Selection

Risk-Free
What you need to know about Stomach Cancer Surgery in Spain
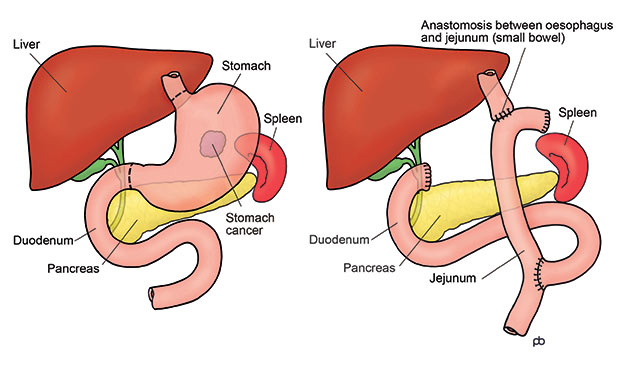
Surgery is a treatment option for numerous different stages of stomach cancer, particularly in its early stages. If a patient has a stage 0, I, II, or III cancer and is generally healthy enough, surgery often offers the only realistic chance for cure.
The aim of surgery is to remove all of cancer in the stomach while keeping as much normal tissue as possible. In some cases, some nearby tissues and lymph nodes may also be removed, depending on the stage and type of stomach cancer. Sometimes the surgeon may need to remove other organs as well.
What does the Procedure Involve?
There are several different types of surgery for stomach cancer. The type of surgery you have will depend on the type and stage of your cancer, as well as its location in your stomach.
Endoscopic resection
Endoscopic resection is used to treat very early-stage tumors that have not spread from the stomach walls. The goal of this procedure is to effectively remove the body of stomach cancer. For some people, this type of procedure is the only treatment needed.
During this procedure, no incision is made in the skin. Instead, your surgeon inserts a flexible tube with a small camera on its end (called an endoscope) through your mouth down into your stomach. Through the endoscope, surgical tools are passed to remove all cancerous tissue and some of the normal stomach wall around it.
Gastrectomy
Gastrectomy is carried out to remove part or all of the stomach while leaving as much healthy tissue as possible. The goal of the surgery is to completely remove cancer from the stomach, as well as the nearby lymph nodes. Gastrectomy is commonly performed on those whose stomach cancer has advanced. There are two types of gastrectomy:
-
Subtotal (partial) gastrectomy – this type of gastrectomy is usually recommended if the cancer is located only in the lower part of the stomach. Sometimes, it is used for cancers that are located only in the upper portion of the stomach as well. Subtotal gastrectomy involves removing part of the stomach, sometimes along with the first part of the small intestine or part of the esophagus. The surgeon may also remove part of the tissue that holds your stomach in place (the omentum). How much of your stomach and other organs removed depends on the position of cancer. After the surgery, you will have a smaller stomach.
-
Total gastrectomy – total gastrectomy is done if cancer has spread throughout the stomach. It is also recommended if the cancer is located near the esophagus in the upper part of the stomach or in the middle of the stomach. During the surgery, your surgeon removes the entire stomach, the omentum, nearby lymph nodes, and sometimes, parts of the nearby organs (such as the esophagus, pancreas, and intestines). In order to enable you to continue swallowing and eating normally, your surgeon then attaches the esophagus to part of the small intestine.
A gastrectomy, both subtotal and total, can be performed in three ways:
-
Laparotomy (open surgery) involves creating a large incision in the abdomen. This procedure may be needed if your abdomen contains scar tissue from previous surgery, making creating a small incision difficult.
-
Laparoscopy (keyhole surgery) involves making several tiny incisions in the skin above the abdomen. Through one incision, the surgeon inserts a laparoscope (a thin, lighted tube with a small camera on its end). Through the other incisions, the surgeon inserts small surgical tools to perform the surgery.
-
Robotic-assisted surgery uses a robotic surgical tool. The surgeon operates the robot using a console displaying a magnified 3-D image of the inside of your abdomen, which has been highlighted with a special fluorescent dye.
Placement of a feeding tube
After stomach cancer surgery, some patients experience trouble taking in enough nutrition. Other treatments, such as radiation therapy and chemotherapy can make the problem even worse. To help you take in enough nutrition, your surgeon can place a tube into the intestine during gastrectomy. The end of this tube remains on the outside of the skin. Through the end of the tube, you can put liquid nutrition directly into the intestine, preventing, and treating malnutrition.
How Long Should I Stay in Spain?
Your length of stay depends on the type of surgery you underwent. In general, you need to stay in the hospital for a few days. Plan to stay in Spain for at least 7 days for initial recovery and follow-up checkups.
What's the Recovery Time?
The recovery time can vary, depending on the type of surgery and the technique your surgeon used. After endoscopic resection, many patients are able to return to work 2-3 days after surgery. For gastrectomy, it generally takes around 4 to 6 weeks until you can resume your normal routine, including work. However, if your doctor uses the laparoscopic technique, the recovery period can be shorter.
What About Aftercare?
Your surgeon will give you a set of post-operative instructions that you need to follow. These include wound care and medications to take. You may need to attend regular follow-up checkups to ensure cancer has not come back.
After stomach cancer surgery, you may need to change your diet and you’re eating patterns. You need to eat smaller, more frequent meals instead of three big meals a day, particularly after total gastrectomy. Your surgeon will advise you to eat a low-carb and high-protein diet to help you feel better after eating.
What's the Success Rate?
The success rate for stomach cancer surgery depends on the stage of cancer and the type of stomach cancer you have. In general, surgery is very effective, particularly in the early stages of stomach cancer.
As with any major surgery, stomach cancer surgery has risks and side effects. These include bleeding, infection, and damage to nearby organs.
Are there Alternatives to Stomach Cancer Surgery?
In many cases, surgery is necessary to treat stomach cancer, so there are no other alternatives. However, your doctor may recommend radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or targeted therapy instead of surgery, but it often depends on the stage of cancer you have. These types of treatments are usually needed along with surgery.
What Should You Expect Before and After the Procedure
Stomach cancer can be life-threatening and cause uncomfortable symptoms. After surgery, the symptoms you felt before should be gone and the chance of your cancer spreading to other organs is reduced. In some cases, you may also be put in remission, meaning no cancer is found in your body.
Whilst the information presented here has been accurately sourced and verified by a medical professional for its accuracy, it is still advised to consult with your doctor before pursuing a medical treatment at one of the listed medical providers
No Time?
Tell us what you're looking for and we'll reachout to the top clinics all at once
Enquire Now

Popular Procedures in Spain
Prices Start From $47

Prices Start From $2,487

Recommended Medical Centers in Spain for procedures similar to Stomach Cancer Surgery

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available
- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available
Stomach Cancer Surgery in and around Spain
About Spain
Historic Spain is home to the third-highest number of UNESCO World Heritage Sites, after Italy and China. Part of the Iberian Peninsula, along with Portugal, Spain also shares borders with France and the less well-known, Andorra. The country itself is made up of several regions, both on the mainland and out at sea, with the Canary Islands closer to Morocco than Spain - they are located in the Atlantic Ocean, whilst the Balearic Islands are a little closer to home, in the Mediterranean Sea. On the mainland there is Central Spain, home to the capital, Madrid, Catalonia in the East, home to the second city, Barcelona, and the Basque Country in the North, to name but a few.
Spain sees an estimated 100,000 medical tourists each year, many of which travel for Stomach Cancer Surgery procedures. The biggest target market is from the UK, accounting for one in four of Spain's 60m annual tourists. An excellent healthcare system combined with warm temperatures and competitive prices means that Spain is now one of the more popular destinations in Europe for medical tourism. The most popular procedures tend to be cosmetic surgery, fertility treatments, bariatric surgery, cardiac surgery, orthopedics, urology, and bone marrow transplants.
Popular Parts of Spain
Spain has diverse landscapes, dynamic cities, influential art, and delightful food.
- Madrid is the capital of Spain. Modern infrastructure and historic neighborhoods blend nicely in the city. Known for its glorious fashion, food, and nightlife, the city has a lively spirit. Rest in El Retiro Park under the sun or take a guided tour in Palacio Real. Tourists who love sports can watch a Real Madrid soccer match.
- Barcelona has a plethora of attractive architecture, unique food beautiful beaches, and a vibrant nightlife. It is the most popular tourist destinations in the country. Visit Picasso Museum, Enjoy Gaudi’s Architecture the church of the Sagrada Família, or visit the Barcelona History Museum and enjoy the beach.
- Valencia is Spain’s third-largest city. The city is filled with an array of art nouveau buildings as well as Gothic and Renaissance monuments. Try all the food that the city offers, especially the famous paella. Be inspired by the stunning Cuidad de las Artes y las Ciencias, a massive building in the old Turia riverbed.
- Palma de Mallorca is a very welcoming city for international tourists. It has a number of historical attractions, Gothic churches, and the beautiful Mediterranean Sea at its feet. Shopping and gastronomic scenes are two of the best things in the city. Tourists can relax in the seafront cafés after a long day.
- Seville is a stunning artistic, cultural, and financial capital of southern Spain. Being a big university town, it has a very youthful vibe everywhere. Spend a day exploring Parque de Maria Luisa, tour Casa de Pilatos, get lost in the maze of Jewish Quarter’s small streets, and discover what the town has to offer on a bike.
- Ibiza is known to have some of the best nightclubs in the world. It is a beautiful island with dozens of amazing things to discover.
Weather and Climate in Spain
Spain has wonderful weather all year-round. Summer starts from June to August and tends to be nice. Tourists can expect warm and sunny weather. The temperature can get as high as 30 °C, sometimes even higher. Summer is the peak season for tourism so prices can increase by up to 50%.
Spring (April to May) and Autumn (September to October) are great times to visit. The weather is mild and perfect to do outdoor activities, although sometimes it can be unpredictable. The country is not as crowded as during summertime.
Winter in Spain is cold but the temperature does not drop too low. The average temperature is between 4 °C to 10 °C. Northern Spain and the mountainous areas sometimes experience snowfall and rain showers.
Getting Around in Spain
The main international airport in Spain is Adolfo Suárez Madrid-Barajas and Barcelona El Prat Airport. Madrid-Barajas is the largest airport in the country. It operates domestic and international flights. The airport connects Madrid with almost every country in the world. It serves several budget airlines such as Iberia Express, Ryanair, and EasyJet. It is the hub for Air Europa and Iberia.
Barcelona El Prat Airport also serves domestic and international connections with almost every country globally. Budget airlines such as Ryanair and WestJet operate flights from this airport. It is the hub for Level and Vueling.
To get to the city center, both airports provide taxis, buses, and metro. Taxis are the most convenient transportation mode but usually more expensive. Tourists who travel to Madrid are advised to buy the Madrid Tourist Travel Pass which can be used on any Metro, bus, or suburban train for just 5 EUR.
Spain has a well-designed public transportation network. Tourists can get around Spain by train. There are high-speed (AVE) and regular service trains (Talgo) for long-distance or medium distance travel, the fares are based on a 1st and 2nd class system. For short destinations, tourists can use local trains. It offers one class of seats and makes a lot of stops. 60-year-old and older travelers can get a discount between 25 to 40 percent for train tickets. Children under the age of 13 also qualified for discounts. Buses are another excellent option. Intercity buses are affordable, clean, and safe.
Renting a car gives more flexibility for tourists. International car rental agencies are widely available in the country. The highway system is easy for foreigners to follow. Parking can be quite hard in some cities and historic towns because it can get really crowded.
Taxis have a reasonable price. Spanish taxi drivers are usually trustworthy and don’t cheat. The taxi can be hailed on the street or from a taxi stand (parade de taxi). Available taxis have green lights or signs that say “libre” on them. Taxis run on meters, but if you’re traveling a long distance, you will have to agree on the fare in advance.
Tourist Visas in Spain
Citizens of the European Union, Norway, Liechtenstein, Iceland, and Switzerland can travel to Spain with their identity cards only. Citizens of Australia, Canada, Israel, Japan, the United States, and New Zealand are granted visa-free entry and can stay for up to 90 days. Other countries can check with their nearest Spanish embassy or consulate. Spain is a member of the Schengen Convention. If you hold a Schengen visa, you cannot extend it.
Additional Information
- Local Currency: the official currency is the euro (EUR). 1 USD converts to 0.85 EUR.
- Money & Payments: ATMs are available. Tourists can withdraw money from ATMs that display the relevant symbols such as Visa and MasterCard with a charge of 1.5% to 2%. Credit and debit cards can be used for most purchases, tourists will often be asked to show a passport. Tipping is optional, tourists can leave small change or up to 5% tip in restaurants.
- Local Language: the official language is Spanish. People in major tourist cities speak good English; it is also widely spoken in coastal resorts.
- Local Culture and Religion: The largest religion in the country is Catholic Christianity with 67.5% of the population follows the religion. There are small groups of Muslims, Jews, Buddhists, Hindus, Pagans, Taoists, and Bahá'ís.
- Public Holidays: Spain celebrates Christian holidays. Known as the country of fiestas and festivals, numerous festivals such as The Holy Week, La Tomatina, and The Fallas of Valencia are hosted annually.
Popular Searches
- Plastic Surgery in Thailand
- Dental Implants in Thailand
- Hair Transplant in Thailand
- Breast Augmentation Thailand
- Gastric Sleeve in Thailand
- Gender Reassignment Surgery in Thailand
- Laser Hair Removal in Bangkok
- Botox in Bangkok
- Dermatology in Bangkok
- Breast Augmentation in Bangkok
- Coolsculpting in Bangkok
- Veneers in Turkey
- Hair Transplant in Turkey
- Rhinoplasty in Turkey
- Stem Cell Therapy in Mexico
- Rhinoplasty in Mexico
- Liposuction in Mexico
- Coolsculpting in Tijuana
- Rhinoplasty in Korea
- Scar Removal in Korea
- Gastric Sleeve in Turkey
- Bone Marrow Transplant in India
- Invisalign in Malaysia
- Plastic Surgery in the Dominican Republic
- Tummy Tuck in the Dominican Republic
- Plastic and Cosmetic Surgery in Poland
- Rhinoplasty in Poland
- Hair Implant in Poland
- Dental Implants in Poland
- IVF in Turkey