Stomach Cancer Surgery in Tunisia
Search and Compare the Best Clinics and Doctors at the Lowest Prices for Stomach Cancer Surgery in Tunisia

Find the best clinics for Stomach Cancer Surgery in Tunisia
No clinics available
Poland offers the best prices Worldwide
Price: $ 512

- Home
- Tunisia
WHY US?
At Medijump, we're making medical easy. You can search, compare, discuss, and book your medical all in one place. We open the door to the best medical providers worldwide, saving you time and energy along the way, and it's all for FREE, no hidden fees, and no price markups guaranteed. So what are you waiting for?

Free

Best Price

Widest Selection

Risk-Free
What you need to know about Stomach Cancer Surgery in Tunisia
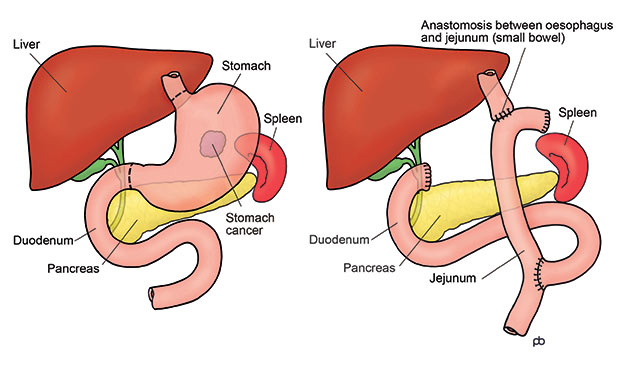
Surgery is a treatment option for numerous different stages of stomach cancer, particularly in its early stages. If a patient has a stage 0, I, II, or III cancer and is generally healthy enough, surgery often offers the only realistic chance for cure.
The aim of surgery is to remove all of cancer in the stomach while keeping as much normal tissue as possible. In some cases, some nearby tissues and lymph nodes may also be removed, depending on the stage and type of stomach cancer. Sometimes the surgeon may need to remove other organs as well.
What does the Procedure Involve?
There are several different types of surgery for stomach cancer. The type of surgery you have will depend on the type and stage of your cancer, as well as its location in your stomach.
Endoscopic resection
Endoscopic resection is used to treat very early-stage tumors that have not spread from the stomach walls. The goal of this procedure is to effectively remove the body of stomach cancer. For some people, this type of procedure is the only treatment needed.
During this procedure, no incision is made in the skin. Instead, your surgeon inserts a flexible tube with a small camera on its end (called an endoscope) through your mouth down into your stomach. Through the endoscope, surgical tools are passed to remove all cancerous tissue and some of the normal stomach wall around it.
Gastrectomy
Gastrectomy is carried out to remove part or all of the stomach while leaving as much healthy tissue as possible. The goal of the surgery is to completely remove cancer from the stomach, as well as the nearby lymph nodes. Gastrectomy is commonly performed on those whose stomach cancer has advanced. There are two types of gastrectomy:
-
Subtotal (partial) gastrectomy – this type of gastrectomy is usually recommended if the cancer is located only in the lower part of the stomach. Sometimes, it is used for cancers that are located only in the upper portion of the stomach as well. Subtotal gastrectomy involves removing part of the stomach, sometimes along with the first part of the small intestine or part of the esophagus. The surgeon may also remove part of the tissue that holds your stomach in place (the omentum). How much of your stomach and other organs removed depends on the position of cancer. After the surgery, you will have a smaller stomach.
-
Total gastrectomy – total gastrectomy is done if cancer has spread throughout the stomach. It is also recommended if the cancer is located near the esophagus in the upper part of the stomach or in the middle of the stomach. During the surgery, your surgeon removes the entire stomach, the omentum, nearby lymph nodes, and sometimes, parts of the nearby organs (such as the esophagus, pancreas, and intestines). In order to enable you to continue swallowing and eating normally, your surgeon then attaches the esophagus to part of the small intestine.
A gastrectomy, both subtotal and total, can be performed in three ways:
-
Laparotomy (open surgery) involves creating a large incision in the abdomen. This procedure may be needed if your abdomen contains scar tissue from previous surgery, making creating a small incision difficult.
-
Laparoscopy (keyhole surgery) involves making several tiny incisions in the skin above the abdomen. Through one incision, the surgeon inserts a laparoscope (a thin, lighted tube with a small camera on its end). Through the other incisions, the surgeon inserts small surgical tools to perform the surgery.
-
Robotic-assisted surgery uses a robotic surgical tool. The surgeon operates the robot using a console displaying a magnified 3-D image of the inside of your abdomen, which has been highlighted with a special fluorescent dye.
Placement of a feeding tube
After stomach cancer surgery, some patients experience trouble taking in enough nutrition. Other treatments, such as radiation therapy and chemotherapy can make the problem even worse. To help you take in enough nutrition, your surgeon can place a tube into the intestine during gastrectomy. The end of this tube remains on the outside of the skin. Through the end of the tube, you can put liquid nutrition directly into the intestine, preventing, and treating malnutrition.
How Long Should I Stay in Tunisia?
Your length of stay depends on the type of surgery you underwent. In general, you need to stay in the hospital for a few days. Plan to stay in Tunisia for at least 7 days for initial recovery and follow-up checkups.
What's the Recovery Time?
The recovery time can vary, depending on the type of surgery and the technique your surgeon used. After endoscopic resection, many patients are able to return to work 2-3 days after surgery. For gastrectomy, it generally takes around 4 to 6 weeks until you can resume your normal routine, including work. However, if your doctor uses the laparoscopic technique, the recovery period can be shorter.
What About Aftercare?
Your surgeon will give you a set of post-operative instructions that you need to follow. These include wound care and medications to take. You may need to attend regular follow-up checkups to ensure cancer has not come back.
After stomach cancer surgery, you may need to change your diet and you’re eating patterns. You need to eat smaller, more frequent meals instead of three big meals a day, particularly after total gastrectomy. Your surgeon will advise you to eat a low-carb and high-protein diet to help you feel better after eating.
What's the Success Rate?
The success rate for stomach cancer surgery depends on the stage of cancer and the type of stomach cancer you have. In general, surgery is very effective, particularly in the early stages of stomach cancer.
As with any major surgery, stomach cancer surgery has risks and side effects. These include bleeding, infection, and damage to nearby organs.
Are there Alternatives to Stomach Cancer Surgery?
In many cases, surgery is necessary to treat stomach cancer, so there are no other alternatives. However, your doctor may recommend radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or targeted therapy instead of surgery, but it often depends on the stage of cancer you have. These types of treatments are usually needed along with surgery.
What Should You Expect Before and After the Procedure
Stomach cancer can be life-threatening and cause uncomfortable symptoms. After surgery, the symptoms you felt before should be gone and the chance of your cancer spreading to other organs is reduced. In some cases, you may also be put in remission, meaning no cancer is found in your body.
Whilst the information presented here has been accurately sourced and verified by a medical professional for its accuracy, it is still advised to consult with your doctor before pursuing a medical treatment at one of the listed medical providers
No Time?
Tell us what you're looking for and we'll reachout to the top clinics all at once
Enquire Now

Popular Procedures in Tunisia
Prices Start From $47

Prices Start From $2,487

Recommended Medical Centers in Tunisia for procedures similar to Stomach Cancer Surgery

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available
Stomach Cancer Surgery in and around Tunisia
About Tunisia
Tunisia is one of the few countries which can cater to everyone and it manages to combine climate, golden beaches, history, and shopping for an “all-around” experience. It has a high standard of healthcare and an excellent reputation for cosmetic surgery. Cosmetic and plastic surgeons are regulated by the Tunisian Ministry of Health and the private clinics have state-of-the-art equipment and English-speaking staff. Tunisia welcomes an ever-increasing number of medical tourists each year, many of whom travel for Stomach Cancer Surgery procedures. Medical Tourists travel from all across the globe, particularly from Europe and neighboring African countries with an inferior healthcare system. Popular medical tourism destinations outside of the capital, Tunis, include Sousse and Mahdia
Popular Parts of Tunisia
- Tunis, the country’s capital, is overflowing with a history that dates from the 4th Century BC. The city is divided into two parts, the old city known as the medina and the new city (or Ville nouvelle in French). Many tourists visit Tunis to see the Archaeological Site of Carthage which is also a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The beautiful Islamic architecture in medina also attracts many tourists to the city.
- Tozeur is known as a home to an enchanting desert oasis, which was a place to rest and refuel for caravans crossing the Sahara. Another main attraction in the city is the medina, where tourists can find lines of beautiful brick-patterned traditional dessert houses. Chott el Djerid, Sahara’s largest salt pan, is a popular day-trip destination.
- Sousse is located on the coast of the Mediterranean Sea. It offers good beaches with a clear blue sea. The city has been fought over by the Romans, Arabs, and Europeans, giving it a colorful history and culture. Sousse Archeological Museum is one of the most visited sites in the country; it has the second largest collection of mosaics in the world.
- Hammamet is the country’s original tourism resort. The city has beautiful gardens filled with oranges, lemons, and other citrus plants. It also has wonderful sandy beaches with crystal clear water. Just like any other city in Tunisia, this city is also brimming with interesting histories. Sites such as The Gafsa Museum and Bardo Museum will give insights about the Islamic faith and culture.
- Douz, also known as “the gateway to the Sahara.” Tourists who want to experience the Sahara Desert come to this city. Take a camel trip or a 4-wheel-drive into the Sahara or see the Museum of the Sahara that has an interesting collection portraying traditional Saharan life.
Weather and Climate in Tunisia
The North of Tunisia has a subtropical Mediterranean climate with mild rainy winters and hot summers. The South and inland areas have a tropical desert climate.
The weather is relatively comfortable throughout the year. Summer starts in June and lasts until August. The average temperature is between 28 °C to 32 °C with July and August being the hottest months. The heat is not as bad on the coast because of the seaside breeze. Be aware that July to September is the jellyfish season.
The heat decreases in autumn and the weather is somewhat more comfortable. There are occasional rain showers in September. The temperature in October can be like summer during day time, but cold at night. October has more rain than September. The season lasts for three months from September to November with an average temperature of around 19 °C to 29 °C.
The weather in winter can be uncertain. The average temperature is between 16 °C and 18 °C, but it can drop to 7 °C at night and below 0 °C in highlands and deserts and a clear sky is rare during this season.
Spring comes in March and the temperature can rise to 20 °C. Mornings and nights are cold; there is still a high probability of rains and thunderstorms at the end of this season.
Getting Around in Tunisia
Tunisia has several international airports. The main airport is Tunic-Carthage International Airport. It has international connections with major European countries and the Middle East. The airport is the hub for Tunisair, Tunisair Express, and Nouvelair. Other airports that have international flights are Enfidha-Hammamet, Monastir Habib Bourguiba, Djerba-Zarzis, and Tabarka-Aïn Draham.
Taxis and buses are available to get to the city center from Tunis Airport. The SNT bus line departs every 30 minutes from the airport, the ticket costs less than 1 TND. There is also the TUT bus which departs every 15 minutes and is more luxurious and expensive.
Airport taxis are available at the airport taxi stand and are usually metered. Always make sure that the driver turns the meter on before riding the taxis. A journey to the city should cost around 5 TND. An extra cost will be added if you have baggage.
Getting around in Tunisia can be done by several transportation modes. Tunisair Express provides domestic flights between Tunis, Tozeur, Djerba, and Gabes. The Train is also available and the national train company in the country is SNCFT that runs modern and comfortable trains from Tunis to Sousse, Sfax, and Monastir. There are three classes of service that tourists can choose. The fare from Tunis to Sousse is between 6 to 10 TND. The long-distance bus is an economical option to travel between big cities such as Tunis, Hammamet, and Nabeul. The buses usually depart every 30 minutes.
Tourist Visas in Tunisia
Citizens of 97 countries (including Australia, China Singapore, the United States, and Russia) can visit and stay in Tunisia for up to 90 days without a visa. Other nationalities are advised to check with their local Tunisia embassy. Tunisia provides an online visa application for nationalities that needs a visa to enter. The eVisa will simplify the process of obtaining travel authorization to enter the country.
Additional Information
-
Local Currency: the local currency is the Tunisian dinar (TND). 1 USD converts to 2.61 TND.
-
Money & Payments: ATMs can be found in most cities and in all tourist areas. Many ATMs have withdrawal limits of 400 TND. Credit cards (MasterCard and Visa) are accepted in major cities and tourist areas. They can be used for shops, car hire, or top-end accommodation. Always make sure to carry cash if you want to travel outside major cities. Tipping is not necessary but will be appreciated.
-
Local Language: Arabic is the official language of Tunisia. French is very common due to the country’s former status as a French protectorate. English is still very limited except in the tourist areas and expensive hotels.
-
Local Culture and Religion: Islam is the major religion with 98% of the population identified as Muslim. There is a small group of Christian and Jews. Since most of the population is Muslim, always remember that the dress code is important in Tunisia.
-
Public Holidays: Tunisia celebrates major Islam holidays. The country hosts several annual festivals throughout the year such as The International Festival of the Sahara, Yasmine Hammamet Festival, and the International Festival of Carthage.
Popular Searches
- Plastic Surgery in Thailand
- Dental Implants in Thailand
- Hair Transplant in Thailand
- Breast Augmentation Thailand
- Gastric Sleeve in Thailand
- Gender Reassignment Surgery in Thailand
- Laser Hair Removal in Bangkok
- Botox in Bangkok
- Dermatology in Bangkok
- Breast Augmentation in Bangkok
- Coolsculpting in Bangkok
- Veneers in Turkey
- Hair Transplant in Turkey
- Rhinoplasty in Turkey
- Stem Cell Therapy in Mexico
- Rhinoplasty in Mexico
- Liposuction in Mexico
- Coolsculpting in Tijuana
- Rhinoplasty in Korea
- Scar Removal in Korea
- Gastric Sleeve in Turkey
- Bone Marrow Transplant in India
- Invisalign in Malaysia
- Plastic Surgery in the Dominican Republic
- Tummy Tuck in the Dominican Republic
- Plastic and Cosmetic Surgery in Poland
- Rhinoplasty in Poland
- Hair Implant in Poland
- Dental Implants in Poland
- IVF in Turkey