Full Body CT Scan in Belgium
Search and Compare the Best Clinics and Doctors at the Lowest Prices for Full Body CT Scan in Belgium
Find the best clinics for Full Body CT Scan in Belgium
No clinics available
United Kingdom offers the best prices Worldwide
Price: $ 23

- Home
- Belgium
WHY US?
At Medijump, we're making medical easy. You can search, compare, discuss, and book your medical all in one place. We open the door to the best medical providers worldwide, saving you time and energy along the way, and it's all for FREE, no hidden fees, and no price markups guaranteed. So what are you waiting for?

Free

Best Price

Widest Selection

Risk-Free
What you need to know about Full Body CT Scan in Belgium
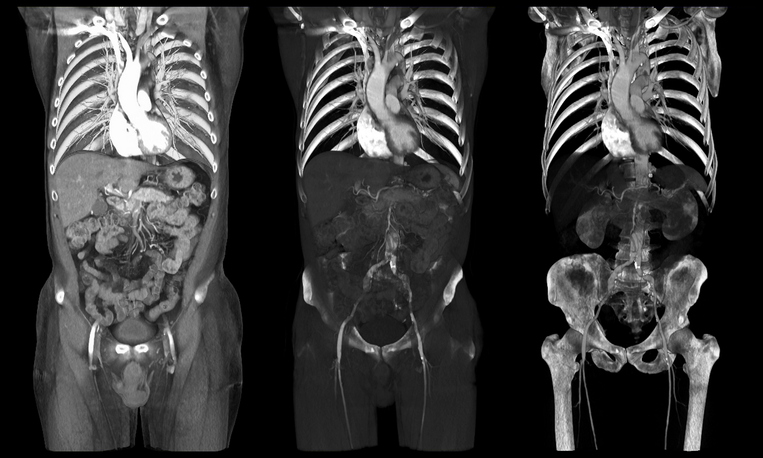
A computerized tomography (CT) scan, sometimes referred to as computerized axial tomography (CAT) scan, is a type of imaging test that uses a combination of sophisticated X-ray technology and a computer to create cross-sectional images of the body. The images produced show more detail than a regular X-ray and can show blood vessels, bones, and soft tissues in various parts of the body. The scan can help your doctor detect a variety of diseases and conditions. In a full-body CT scan, the test is used to visualize virtually all parts of the body.
A full-body CT scan can analyze three major areas of the body: the heart, the lungs, and the abdomen. This test is commonly used on those who already have cancer, to see if it has spread to other parts of the body. It is also helpful in an emergency situation to help your doctor examine a major injury. Besides, the test can be used to:
-
Diagnose disorders of the muscle and the bone, such as fractures and bone tumors
-
Pinpoint the exact location of an infection, blood clot, or tumor
-
Detect and monitor diseases and conditions that may be present in your body
-
Detect internal bleeding and internal injuries.
Your doctor may also recommend a full-body CT scan if you are at a high risk of lung cancer.
What does a Full Body CT Scan Procedure Involve?
During a full-body CT scan, you will have to lie flat on your back on a motorized table that can slide through the doughnut-shaped CT scanner machine. Straps, pillows, and a special cradle may be used to help you stay in the correct position and remain still during the exam. In some cases, a contrast material may be used. It will be injected through an intravenous line (IV) or swallowed.
To determine the correct position for the scans, the table will move quickly through the scanner. Then, during the actual CT scanning, the table will move slowly through the machine and it may take several passes. When the motorized table moves you into the machine, the X-ray tube and detectors will rotate around you. Several images of thin slices of your body are taken in each rotation. The images are then sent to a computer, where they are combined to
The radiographer will operate the machine from a separate room. They can see and hear you, and you will be able to communicate with them during the scan via intercom. They may ask you to hold your breath at certain parts of the scan because you need to stay completely still. Any motion, including body movements and breathing, can blur the scan images. The radiographer may also lower, raise, or tilt the table to create the correct angle for the X-rays.
No anesthesia is involved in a full-body CT scan as it is not painful. However, children who cannot stay still may be sedated.
How Long Should I Stay in Belgium for a Full Body CT Scan Procedure?
You may be allowed to leave the hospital on the same day as your full-body CT scan. However, since the results will not be given to you immediately, it is advisable that you stay in Belgium for 5 to 7 days, or until the results are ready. Once the results are ready, you will have to attend a follow-up appointment to discuss them with your doctor.
What's the Recovery Time for Full Body CT Scan Procedures in Belgium?
Full-body CT scans do not require any recovery time. You can return to your daily activities, go to work, drink, drive, eat, and drink as normal straight away.
What sort of Aftercare is Required for Full Body CT Scan Procedures in Belgium?
If a contrast material is used, you will have to drink lots of fluids to help your kidneys flush out the contrast material from your body. If not, there are no restrictions or special aftercare following the procedure.
What's the Success Rate of Full Body CT Scan Procedures in Belgium?
A full-body CT scan has the potential to be inaccurate. A cancer diagnosis based on a CT scan has up to 30% inaccuracy rates. In addition, the procedure is not recommended for those without symptoms.
A full-body CT scan carries some potential risks. During the procedure, your body will be exposed to ionizing radiation. While low doses of radiation in the procedure have not been revealed to cause any harm in the long-term, much greater doses may slightly increase your risk of cancer. The procedure can also harm unborn babies. Therefore, make sure to tell your doctor if you are pregnant.
In some cases, the contrast material can cause allergic reactions, which may result in a rash or itchiness.
Are there Alternatives to Full Body CT Scan Procedures in Belgium?
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) scans is the main alternative to a full-body CT scan. MRI scans are currently being evaluated for their possible value in screening. One major benefit of the procedure is that they do not expose you to ionizing radiation. However, they tend to be more expensive than a full-body CT scan.
What Should You Expect Before and After the Procedure
Before a full-body CT scan, you may experience unexplained symptoms or have a high risk of developing certain diseases. After the procedure, your doctor should find out if there are any abnormalities present in your body. If they do find an abnormality, they may order more imaging procedures to confirm their diagnosis or discuss the best treatment/management plan for you.
Whilst the information presented here has been accurately sourced and verified by a medical professional for its accuracy, it is still advised to consult with your doctor before pursuing a medical treatment at one of the listed medical providers
No Time?
Tell us what you're looking for and we'll reachout to the top clinics all at once
Enquire Now

Popular Procedures in Belgium
Prices Start From $42

Prices Start From $4

Prices Start From $11

Prices Start From $11

Recommended Medical Centers in Belgium for procedures similar to Full Body CT Scan

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available
Full Body CT Scan in and around Belgium
Belgium is one of the smallest and most densely populated countries in Europe and has some of Europe’s finest cuisine, including the creamiest chocolates and a wide variation of beers. In addition, it is home to extensive beaches, postcard-worthy dunes, historic cities, and beautiful countryside, with belfries, castles, and carnivals. Belgium has enjoyed a growing reputation for being excellent medical tourism as well as the country boasts immaculate clinical standards. The medical centers in the country offer a wide range of specializes treatments, short waiting time, highly-trained medical professionals, and considerably lower medical costs. Orthopedics and heart surgery are the most sought after procedures in Belgium.
Popular Parts of Belgium
Brussels is the capital of Belgium, as well as home to European Union official seats and NATO headquarters. Here, visitors can see Europe’s grandest squares, visit the beloved statue of a little boy peeing into a basin (Manneken Pis), explore Musées Royaux des Beaux-Arts, and admire the magnificent Grand Palace. Bruges, a pickled Gothic city, is also worth a visit. The key attractions in the city are the 14th-century town hall, the Cathedral of the Holy Savior, and the Belfry Tower. Other popular cities include Antwerp and Ghent. While Antwerp is famous for its fashion and excellent museums, Ghent is best known for its historic quarter and stunning Van Eyck altarpiece in its colossal cathedral.
Weather and Climate in Belgium
Belgium has four distinct seasons. Summer in the country is relatively short, starting in July and ending in August. The season is warm, with bearable heat and some intermittent rain. Winter comes in November and extends until March. It can get rather wet and chilly during this season, with an average temperature of around 3 - 7°C. Spring (April – June) and autumn (September – October) are generally nice and warm, with an average temperature of around 10 - 15°C.
Getting around in Belgium
The main international airport in Belgium is Brussels Airport. It serves flights to many major cities around the world, including Copenhagen, Doha, London, New York, Atlanta, Casablanca, and Bangkok. Since Belgium is a small country, there are no domestic flights. The public transport system in the country is extremely well-organized and reasonably priced. The best way to get around the country is by train. The trains are affordable, fast, frequent, very punctual, and have a comprehensive network of lines. Buses tend to be used in conjunction with train services, so you will likely need a train-bus combination when traveling, especially to rural areas. Inside cities, the transport systems are centered on buses, but there are also metro and trams in Brussels and Antwerp. Taxis are plentiful in all cities and ensure to hire metered official taxis, which have standard fares.
Tourist Visas in Belgium
Belgium is part of the Schengen Area, so nationals of EU/EEA countries do not need a visa to visit the country regardless of their length of stay or purpose of travels. Citizens of 62 countries, including Canadian, Australian, and US nationals, can stay in the country without a visa for up to 90 days. Belgium Visa for Medical reasons is available for people who need to obtain medical care in the country.
Additional Information
- Local Currency: Belgium adopted the euro (€) in 2002. The exchange rate from US$1 is around €0.85 (€1 is around US$1.17).
- Money & Payments: All towns and cities have cashpoints that are compatible with international banking networks. Credit Cards, particularly MasterCard and Visa, are widely accepted in major cities and towns. Always have some cash on you when traveling to smaller villages. Tipping is not standard practice but appreciated.
- Local Language: Dutch, German, and French are the official languages in Belgium. English is widely spoken.
- Local Culture and Religion: About 65% of the population is Christian, with a large portion adhere to Roman Catholicism. There are also some small communities of Jewish, Muslim, and Buddhist.
- Public holidays: Some important public holidays in Belgium include New Year’s Day, Easter Monday, Ascension Day, Whit Monday, Independence Day, and Christmas Day.
Popular Searches
- Plastic Surgery in Thailand
- Dental Implants in Thailand
- Hair Transplant in Thailand
- Breast Augmentation Thailand
- Gastric Sleeve in Thailand
- Gender Reassignment Surgery in Thailand
- Laser Hair Removal in Bangkok
- Botox in Bangkok
- Dermatology in Bangkok
- Breast Augmentation in Bangkok
- Coolsculpting in Bangkok
- Veneers in Turkey
- Hair Transplant in Turkey
- Rhinoplasty in Turkey
- Stem Cell Therapy in Mexico
- Rhinoplasty in Mexico
- Liposuction in Mexico
- Coolsculpting in Tijuana
- Rhinoplasty in Korea
- Scar Removal in Korea
- Gastric Sleeve in Turkey
- Bone Marrow Transplant in India
- Invisalign in Malaysia
- Plastic Surgery in the Dominican Republic
- Tummy Tuck in the Dominican Republic
- Plastic and Cosmetic Surgery in Poland
- Rhinoplasty in Poland
- Hair Implant in Poland
- Dental Implants in Poland
- IVF in Turkey