Gallbladder Cancer Treatment in Munich
Search and Compare the Best Clinics and Doctors at the Lowest Prices for Gallbladder Cancer Treatment in Munich

Find the best clinics for Gallbladder Cancer Treatment in Munich
No pricing info available
Ukraine offers the best prices Worldwide
Price: $ 2,487
University Hospital of Munich (LMU), can be found in Professor Huber Platz, Munich, Germany and offers its patients Gallbladder Cancer Treatment procedures as well as 223 other procedures, across 26 different procedure categories. At present, there is no pricing information for Gallbladder Cancer Treatment procedures at University Hospital of Munich (LMU). The pricing information is quite specialised, so it's only available on request. Currently, there's no information available about the doctors at the Hospital, and University Hospital of Munich (LMU) is not accredited by any recognised accreditations institutions.
WHY US?
At Medijump, we're making medical easy. You can search, compare, discuss, and book your medical all in one place. We open the door to the best medical providers worldwide, saving you time and energy along the way, and it's all for FREE, no hidden fees, and no price markups guaranteed. So what are you waiting for?

Free

Best Price

Widest Selection

Risk-Free
What you need to know about Gallbladder Cancer Treatment in Munich
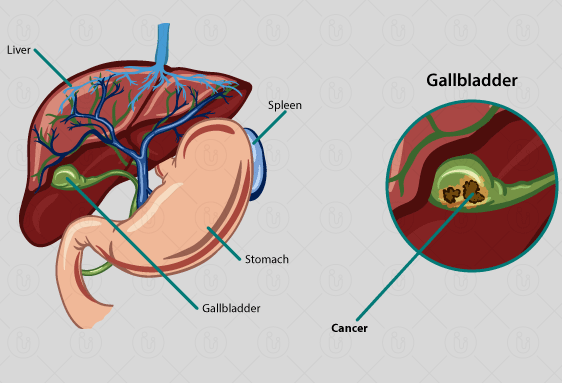
Different types of treatments are available to patients with gallbladder cancer. The main types of treatment include surgery, radiation therapy, and treatment to help with symptoms. The type of treatment that is best for you depends on several factors, including the type of gallbladder cancer you have, the stage of cancer, your overall health, and your preferences. During your gallbladder cancer treatment, you will be looked after by a team of doctors who specialize in different aspects of treatment, including a medical oncologist, a radiation oncologist, a gastroenterologist, and a surgeon.
What does the Procedure Involve?
Surgery is the main treatment for early-stage gallbladder cancer. The following are types of surgery performed to treat gallbladder cancer:
-
Cholecystectomy is a surgical procedure to remove the gallbladder. In some cases, a small amount of liver that surrounds the gallbladder may also be removed (called an extended cholecystectomy).
-
Radical gallbladder resection involves the removal of the gallbladder, a part of the liver near the gallbladder, all or part of the ligaments between the intestines and the liver, the common bile duct, as well as the lymph nodes around the pancreas and blood vessels near the area.
Surgery is generally performed under general anesthetic, so you will not feel anything throughout the procedure.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy X-rays or other particles to destroy cancer cells or to stop them from growing. There are two types of radiation therapy: external and internal. External radiation therapy uses a machine outside of the body, while internal radiation therapy uses a radioactive substance sealed in a device that is placed near or directly into cancer. The most common type of radiation therapy for gallbladder cancer is external radiation therapy.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses drugs to stop cancer cells from dividing. It can also kill cancer cells. The drug can be injected into a vein or muscle or taken by mouth. In some cases, the drugs may also be placed directly into the affected organ.
Treatment to help with symptoms
Also known as palliative care, this type of treatment aims to slow down cancer and to help you manage symptoms that may occur. For instance, if your bile ducts are blocked due to advanced gallbladder cancer, your surgeon can place a stent in a duct in order to hold it open or reroute bile ducts around the blockage.
How Long Should I Stay in Munich?
For surgical procedures, you need to stay in the hospital for 1 to 3 days and stay in Munich for at least 7 to 14 more days for follow-up checkups. For radiation therapy and chemotherapy, your length of stay depends on your treatment plan (how many cycles of therapy you need).
What's the Recovery Time?
The recovery time for surgical procedures may take 2 to 6 weeks, depending on the type of surgery you underwent and the technique your surgeon used. Side effects after radiation therapy and chemotherapy usually subside within several weeks or months.
What About Aftercare?
Your medical team will give you a set of aftercare instructions after any type of treatment. It is important that you follow all of the instructions carefully to avoid complications. The instructions may include a special diet, light exercises, wound care (for surgical procedures), and restrictions.
Make sure to eat a healthy and balanced diet, avoid bad habits (such as smoking), and exercise regularly after you have recovered. You will also need checkups with your doctor for the rest of your life. Regular medical care is important to stay healthy. Regular checkups are necessary to ensure cancer has not come back.
What's the Success Rate?
Gallbladder cancer treatment can be effective and successful. In many cases, treatments may even put you in remission (when cancer cannot be detected in the body and there are no symptoms).
Surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy all come with potential risks and side effects. These include infection, bile leakage, and damage to a bile duct, bleeding, swelling, blood clots, heart problems, pneumonia, hematoma, nausea, vomiting, and hair loss.
Are there Alternatives to Gallbladder Cancer Treatment?
Some people choose to take part in a clinical trial. A clinical trial is a research study that is used to obtain more information on new treatments or to improve current treatments. Currently, treatments called radiation sensitizers are being tested. Radiation sensitizers include hyperthermia therapy (a treatment in which high temperatures are used to kill cancer cells) and radiosensitizers (a treatment that involves the use of drugs that can make tumor cells more sensitive to radiation therapy). Patients who take part in clinical treatment help improve the way cancer will be treated in the future.
What Should You Expect Before and After the Procedure
Before you receive treatment, your gallbladder cancer can cause uncomfortable symptoms, may spread to other parts of the body, and may even become dangerous. After treatment, your chance of surviving the cancer is increased. In some cases, you may even be put in remission, meaning no cancer cells are found in your body.
Whilst the information presented here has been accurately sourced and verified by a medical professional for its accuracy, it is still advised to consult with your doctor before pursuing a medical treatment at one of the listed medical providers
No Time?
Tell us what you're looking for and we'll reachout to the top clinics all at once
Enquire Now

Popular Procedures in Munich
Prices Start From $961

Prices Start From $32

Prices Start From $2,104

Prices Start From $2,487

Recommended Medical Centers in Munich for Gallbladder Cancer Treatment

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available
Gallbladder Cancer Treatment in and around Munich
About Munich
Munich is the largest city in Southern Germany and it is one of a few places on earth where traditional and modern sit side by side, with its royal palaces and high-tech cars. Known as the ‘city of art and beer,’ this city is famous for its annual beer festival known as Oktoberfest. What most people do not realize is that Munich is also one of the world’s most famous medical tourism destination. Thanks to the famous German education system that creates skilled specialists, as well as state-of-the-art medical centers that invest in the latest medical technology, medical tourism in this city is a booming business that continues to grow at a fast rate. International patients usually travel to the city for quality rather than the price.
Popular Parts of Munich
Munich boasts a beautiful historic center, amazing German food, large parks and gardens, and beer halls packed with welcoming people. Visitors can explore numerous historical buildings, such as the Church of St. Peter and Frauenkirche. These two buildings have been around for centuries and are located in Munich’s Old Town. One of the most popular attractions in the city is Alte Pinakothek, which is an important art museum that houses over 800 works from the 14th – 18th centuries from German masters. Those who want to have a picnic, hike, simply relax or even try surfing should visit the English Garden. Other popular places include Dachau Concentration Camp, Nymphenburg Palace, BMW Museum, and Deutsches Museum.
Transport in Munich
The international airport of Munich is Munich Airport, which is the second-busiest airport in Germany in terms of passenger traffic. It serves international flights from many cities around the world, including Dubai, Bangkok, and Atlanta. Munich has a comprehensive network of public transportation that will take visitors virtually anywhere around the city. The most common transit system is the U-Bahn, which is a fast and easy underground subway system. Buses, trams, and commuter trains are also available and each has a vast network. Taxis are easy to hail, reliable, and safe. However, they are a bit pricey and Uber operates in Munich.
Visas in Munich
As a member of the Schengen Area, Germany allows citizens of several countries, including Australia, New Zealand, the US, and Poland to enter and stay in the country without a visa for up to 90 days. Citizens of other countries not listed in the visa-free entry need to obtain a visa to visit the country. Always check the requirements for Germany Visa Application before applying.
Weather in Munich
From June to August is the summer, which is a popular time to enjoy outdoor activities as the temperatures hover around 24°C. On very hot days, the temperatures can reach 30°C. Autumn (September – October) and spring (March-May) has pleasant weather with mild temperatures. Winter can be very cold, with temperatures dropping as low as -10°C.
Additional Info
- Local Currency: Euro (EUR) is the official currency. 1 EUR is approx. 1.12 USD.
- Money & Payments: ATMs are easy to find. Credit cards are not widely accepted and tipping is common practice.
- Local Language: The official language is German. Many people, particularly in tourism areas, understand English to some extent.
- Local Culture and Religion: Christianity is the largest religion in the city, followed by Islam, Buddhism, Hinduism, and Judaism.
- Public Holidays: Munich celebrates numerous holidays, including New Year’s Day and Christmas Day. It also hosts several festivals throughout the year, such as Oktoberfest in October.
Popular Searches
- Plastic Surgery in Thailand
- Dental Implants in Thailand
- Hair Transplant in Thailand
- Breast Augmentation Thailand
- Gastric Sleeve in Thailand
- Gender Reassignment Surgery in Thailand
- Laser Hair Removal in Bangkok
- Botox in Bangkok
- Dermatology in Bangkok
- Breast Augmentation in Bangkok
- Coolsculpting in Bangkok
- Veneers in Turkey
- Hair Transplant in Turkey
- Rhinoplasty in Turkey
- Stem Cell Therapy in Mexico
- Rhinoplasty in Mexico
- Liposuction in Mexico
- Coolsculpting in Tijuana
- Rhinoplasty in Korea
- Scar Removal in Korea
- Gastric Sleeve in Turkey
- Bone Marrow Transplant in India
- Invisalign in Malaysia
- Plastic Surgery in the Dominican Republic
- Tummy Tuck in the Dominican Republic
- Plastic and Cosmetic Surgery in Poland
- Rhinoplasty in Poland
- Hair Implant in Poland
- Dental Implants in Poland
- IVF in Turkey
