Hysterosalpingography (HSG) in Austria
Search and Compare the Best Clinics and Doctors at the Lowest Prices for Hysterosalpingography (HSG) in Austria

Find the best clinics for Hysterosalpingography (HSG) in Austria
No clinics available
Tunisia offers the best prices Worldwide
Price: $ 161

- Home
- Austria
WHY US?
At Medijump, we're making medical easy. You can search, compare, discuss, and book your medical all in one place. We open the door to the best medical providers worldwide, saving you time and energy along the way, and it's all for FREE, no hidden fees, and no price markups guaranteed. So what are you waiting for?

Free

Best Price

Widest Selection

Risk-Free
What you need to know about Hysterosalpingography (HSG) in Austria
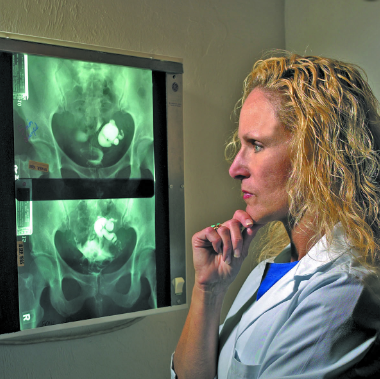
Hysterosalpingography (HSG) is a procedure that uses a special form of X-ray to look at the fallopian tubes and uterus. It is a noninvasive medical test that is often used to find out why you are having difficulty conceiving. The doctor will check if the fallopian tubes are fully or partially blocked and if the inside of the uterus is normal.
Doctors also recommend HSG to examine repeated miscarriages that may be caused by congenital or acquired uterine problems, such as adhesions, endometrial (uterine) polyps, uterine fibroids, congenital problems (uterine anomalies), tumors. In addition, HSG can check the effects of tubal surgery, including:
-
Blockage of the fallopian tubes caused by scarring or infection
-
Reopening of the fallopian tubes after sterilization or a blockage caused by a disease
-
Closing of the fallopian tubes after sterilization procedures.
What does a Hysterosalpingography (HSG) Procedure Involve?
During HSG, you will have to lie on your back with your knees bent on a table under an X-ray imager called a fluoroscope. Then, a device called a speculum will be inserted into your vagina. This device holds the walls of the vagina apart, keeping it open and allowing your doctor to view the cervix. The cervix is then cleaned. In most cases, no sedation is used during the procedure, but your doctor may inject local anesthesia to the end of the cervix to numb the area. You may feel a slight pinch as this is done.
Next, a contrast medium will be placed in the uterus and fallopian tubes. A contrast medium is a fluid containing a dye that can show up the structures of your body on an X-ray screen. The dye can outline the inner size and shape of your uterus and fallopian tubes. Your doctor can also see how the dye moves through your body structures.
To place the contrast, the cervix is grasped with a special device to hold it steady. Then, an instrument called a cannula is inserted into the cervix. Through the cannula, your doctor gently fills your uterus with the contrast. After that, your doctor will remove the speculum, and as the contrast medium fills your uterus and tubes, images are made with the fluoroscope X-ray. You may be asked to move around so that your doctor can get side views. It is normal to feel cramping during this part.
Finally, once the images are taken, your doctor will remove the cannula.
How Long Should I Stay in Austria for a Hysterosalpingography (HSG) Procedure?
HSG is an outpatient procedure, so you should be able to leave the hospital on the same day. In most cases, you can get the test results on the same day and discuss the results with your doctor right away, so you do not have to stay in Austria any longer than you wish to. However, if the results are not immediately ready, plan to stay in the country for several days. Your doctor should give you the details.
What's the Recovery Time for Hysterosalpingography (HSG) Procedures in Austria?
You can resume your normal activities, including work, immediately after HSG. However, you should refrain from sexual intercourse for 2 to 3 days.
What sort of Aftercare is Required for Hysterosalpingography (HSG) Procedures in Austria?
It is also important to note that you might have some vaginal spotting, cramps, stomach discomfort, and dizziness for a few days following the procedure. You can use pads for the vaginal discharge, but make sure to avoid using a tampon. Your doctor may give you antibiotics to prevent an infection and pain medicine to help you with any cramps and discomfort. If your doctor does not prescribe you pain medicine, you can take over-the-counter pain relievers.
What's the Success Rate of Hysterosalpingography (HSG) Procedures in Austria?
HSG is a very safe procedure with high success rates. However, there are some complications that the procedure carries and they only occur with 1% of patients. These complications include infection, radiation exposure, fainting, allergic reaction to the contrast material, and spotting. Injury to your uterus or pelvic injury is possible as well.
The procedure is generally considered as effective and accurate most of the time. However, a small study revealed a 35% incident of false negatives. This means that the results showed a normal uterine shape, but other tests showed abnormalities. Also, 15% of women who undergo this procedure have a false-positive, meaning the results showed abnormalities when it is actually normal.
Are there Alternatives to Hysterosalpingography (HSG) Procedures in Austria?
The following procedures can give your doctor similar information as HSG:
-
Hysteroscopy can provide a detailed view of the inside of your uterus, but it cannot give information about your fallopian tubes.
-
Laparoscopy can show if the fallopian tubes are open.
Sonohysterography can show the insides of your uterus. However, as with hysteroscopy, it cannot show whether your fallopian tubes are blocked.
What Should You Expect Before and After the Procedure
Before HSG, you may have trouble conceiving or had two or more miscarriages, or you just underwent some tubal sterilization procedures. After the procedure, your doctor should be able to find any abnormalities that are causing the problem. The results will be able to help you and your doctor creates a treatment plan. If you have HSG because you have some tubal sterilization procedures before, the results will be able to tell if your fallopian tubes have been completely blocked.
Whilst the information presented here has been accurately sourced and verified by a medical professional for its accuracy, it is still advised to consult with your doctor before pursuing a medical treatment at one of the listed medical providers
No Time?
Tell us what you're looking for and we'll reachout to the top clinics all at once
Enquire Now

Popular Procedures in Austria
Prices Start From $530

Prices Start From $0

Prices Start From $242

Prices Start From $683

Recommended Medical Centers in Austria for procedures similar to Hysterosalpingography (HSG)

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available
Hysterosalpingography (HSG) in and around Austria
Austria is a mountainous landlocked country in south-central Europe. Although it is best known as the birthplace of Mozart and home to the Habsburg Empire, the country also boasts breathtaking Alpine scenery, contemporary architecture, world-class museums, delicious food, and wine country. Austria is also known to have one of the best healthcare systems in the world, making it a popular destination for international medical tourists. Many people, particularly from other European countries and Asia, come to Austria to receive medical care in one of its many internationally acclaimed medical centers, two of which are accredited by JCI. These medical centers feature cutting-edge technology and first-class facilities.
Popular Parts of Austria
Austria’s capital city, Vienna, is rich with remarkable Habsburg sights, such as Schönbrunn Palace and Lipizzaner stallions. It is also home to the Mozart Museum, St. Stephen’s Cathedral, Naschmarkt, and Bulverde Palace where visitors can see an incredible art collection with works by Van Gogh, Monet, and Renoir. Salzburg is another popular city in the country. This city is frequented by fans of Mozart and the “Sound of Music.” It also boasts beautiful Baroque churches, a dramatic castle, and a stunning old town full of winding lanes. Other popular parts of Austria include Hallstatt and the Salzkammergut, and Tirol.
Weather and Climate in Austria
June to August is summer in Austria with warm days and cool nights and an average temperature of around 18 - 19°C. Summer mornings are usually sunny, but thunderstorms can sometimes break out in the afternoon. Winter in Austria, from November to March, can be very cold as the temperatures plummet to an average of -1 to 5°C. Spring and autumn are generally nice and incredibly beautiful.
Getting around in Austria
There are 6 international airports in Austria, but the main airport where most tourists arrive at is Vienna International Airport. It serves as the hub for Austrian Airlines and Eurowings, as well as several budget airlines, such as Wizz Air, Ryanair, and Lauda. This airport connects Austria with many cities in other European countries, North America, Africa, and Asia. Getting around Austria is fairly easy since it's public transport system is fast, efficient, and reaches even remote regions. Internal flights are available, but given the size of the country, it is rarely necessary. The country’s national railway system (ÖBB) is integrated with the Postbus services. Cheaper bust options, such as the Flexibus, are available as well. Inside major cities, an extensive system of light rail, metro, bus, and tramway services are available. Taxis are reliable and relatively affordable.
Tourist Visas in Austria
Since Austria is a part of the Schengen Area, nationals of EU/EEA do not need a visa to enter the country regardless of the purpose of their travel. Citizens of about 62 countries are exempt from a visa to travel to Austria, including the US, Canada, Australia, and South Korea. Unless you are a citizen of these 62 countries, you will need a visa to visit Austria.
Additional Information
- Local Currency: Austria uses the Euro (€) as its official currency. €1 converts to approximately US$1.17.
- Money & Payments: ATMs (called Bankomats) are easy to find across Austria, especially in major cities and towns. Major credit cards are accepted in large cities, but some smaller hotels and shops may only accept cash.
- Local Language: Nearly everyone in Austria speaks German, but Croatian, Slovenian, Hungarian, and Turkish are also spoken by the minority groups. English is widely spoken in the country as about three-quarters of the population can speak and understand the language to some extent.
- Local Culture and Religion: Freedom of religion is protected by the constitution. Around 64% of the population identifies as Roman Catholic. Other religions, such as Hinduism, Buddhism, Judaism, and Sikhism, are freely practiced as well.
- Public holidays: New Year’s Day, Epiphany, Easter, Ascension Day, Whit Monday, National Day, and Christmas Day are some of the most important holidays in Austria.
Popular Searches
- Plastic Surgery in Thailand
- Dental Implants in Thailand
- Hair Transplant in Thailand
- Breast Augmentation Thailand
- Gastric Sleeve in Thailand
- Gender Reassignment Surgery in Thailand
- Laser Hair Removal in Bangkok
- Botox in Bangkok
- Dermatology in Bangkok
- Breast Augmentation in Bangkok
- Coolsculpting in Bangkok
- Veneers in Turkey
- Hair Transplant in Turkey
- Rhinoplasty in Turkey
- Stem Cell Therapy in Mexico
- Rhinoplasty in Mexico
- Liposuction in Mexico
- Coolsculpting in Tijuana
- Rhinoplasty in Korea
- Scar Removal in Korea
- Gastric Sleeve in Turkey
- Bone Marrow Transplant in India
- Invisalign in Malaysia
- Plastic Surgery in the Dominican Republic
- Tummy Tuck in the Dominican Republic
- Plastic and Cosmetic Surgery in Poland
- Rhinoplasty in Poland
- Hair Implant in Poland
- Dental Implants in Poland
- IVF in Turkey