Laryngoscopy in Tokyo
Search and Compare the Best Clinics and Doctors at the Lowest Prices for Laryngoscopy in Tokyo
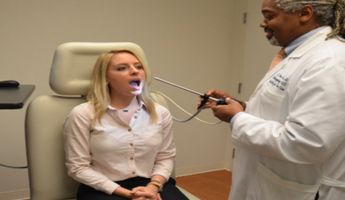
Find the best clinics for Laryngoscopy in Tokyo
No pricing info available
Morocco offers the best prices Worldwide
Price: $ 111
The University Hospital of Tokyo, located in Chome Yushima, Tokyo, Japan offers patients Laryngoscopy procedures among its total of 286 available procedures, across 30 different specialties. Currently, there's no pricing information for Laryngoscopy procedures at The University Hospital of Tokyo, as all prices are available on request only. There is currently a lack of information available on the specialists practicing at the Hospital, and they are not accredited by any recognized accreditations institutes
WHY US?
At Medijump, we're making medical easy. You can search, compare, discuss, and book your medical all in one place. We open the door to the best medical providers worldwide, saving you time and energy along the way, and it's all for FREE, no hidden fees, and no price markups guaranteed. So what are you waiting for?

Free

Best Price

Widest Selection

Risk-Free
What you need to know about Laryngoscopy in Tokyo
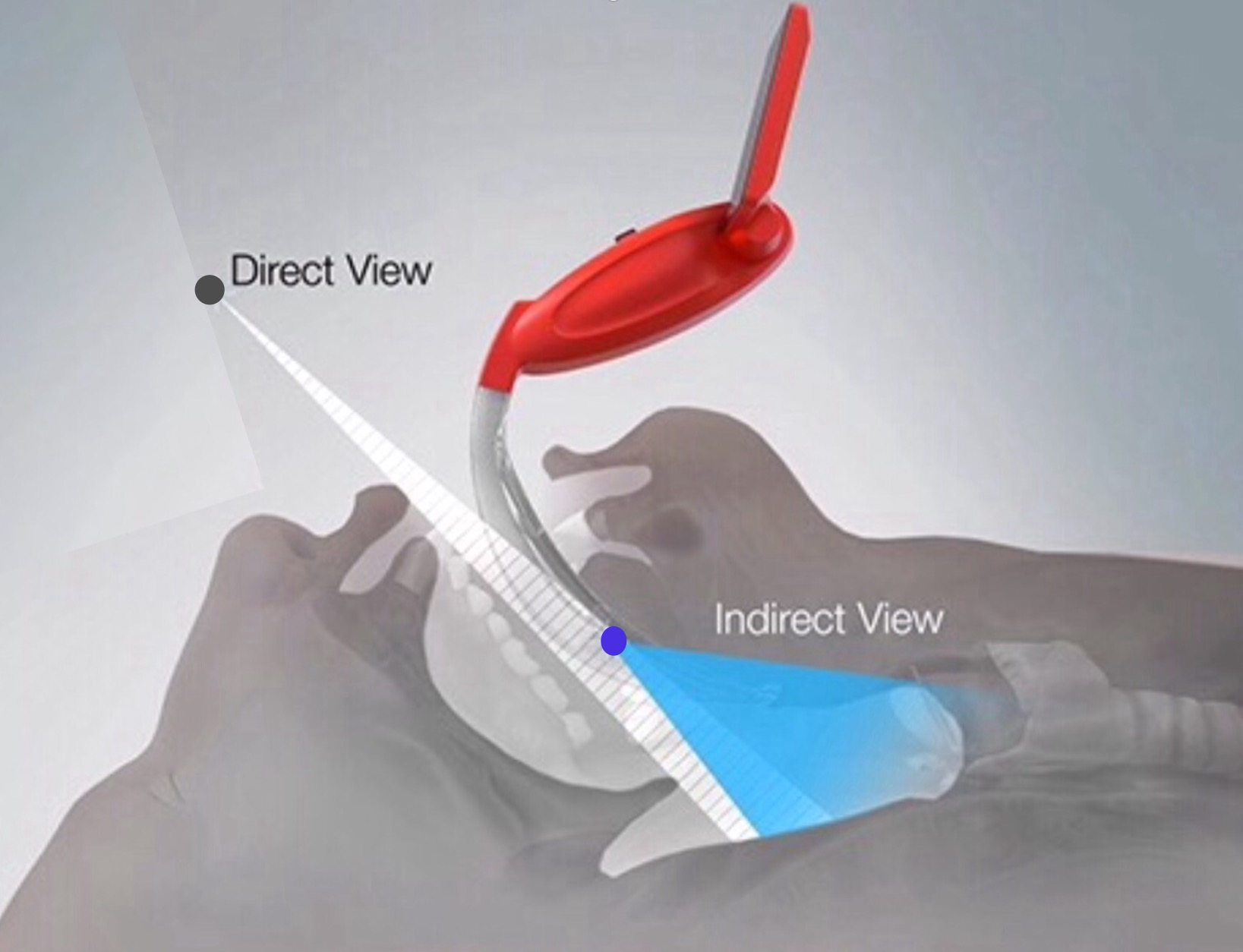
Laryngoscopy is a procedure that gives your doctor a close-up view of your larynx (voice box), including the vocal cords and nearby structures such as the back of the throat, using a special scope called a laryngoscope. There are several reasons why you might need a laryngoscopy, including:
-
To look for the causes of symptoms in the larynx or throat, such as persistent cough, bloody cough, hoarseness, bad breath, throat pain, narrowing of the throat (strictures or stenosis), persistent earache, difficulty swallowing, as well as mass or growth in the throat.
-
To take biopsy samples of any abnormal areas in the vocal cords or nearby parts of the throat. The samples are then examined closely in a laboratory to find out if it contains cancer cells.
-
To treat certain problems in the larynx, including some early stages of cancers.
-
To remove a foreign object from your throat.
What is the cost of Laryngoscopy in Tokyo?
Pricing is subject to fluctuation, influenced by an array of elements such as the geographical whereabouts of the facility, proficiency of the healthcare provider, intricacy of the situation, and the extent of insurance. There may be certain therapeutic centers that propose bundled deals, comprised of post-treatment follow-ups, presenting a valuable alternative. One must not overlook that even though pricing plays a substantial role, it shouldn't detract from the superiority of treatment. Pondering on the skills and know-how of the medical practitioner is vital to attaining optimal results.
What does a Laryngoscopy Procedure Involve?
The laryngoscopy procedure may be done in different ways. There are a few options such as indirect laryngoscopy, direct fiber-optic laryngoscopy, and direct laryngoscopy.
In indirect laryngoscopy, you will sit up straight on a high back chair. Local anesthesia or numbing medicine will be sprayed on your throat so you will not feel anything. Your tongue will be covered with gauze and will be moved to one side to stop it from blocking your doctor’s view. Your doctor will then insert the small mirror into your throat and explore the area. Although your throat is numbed, having a mirror inserted into your throat may still make you gag. Sometimes, your doctor may ask you to make a certain sound in order to make your larynx move. If your doctor found a foreign object in your throat, they will remove it.
Sometimes called flexible laryngoscopy, direct fiber-optic laryngoscopy uses a small telescope attached at the end of a cable, which can go up to your nose and down into your throat. In this type of laryngoscopy, your doctor will give you a numbing medicine for your nose so you will not feel anything. In some cases, your doctor may use a decongestant to open your nasal passages. As in indirect laryngoscopy, you may gag during direct fiber-optic laryngoscopy as well.
Direct laryngoscopy is the most involved type of laryngoscopy. During this procedure, your doctor will push a laryngoscope (a small hand tool that allows your doctor to look into your larynx and other surrounding areas of your throat) down your tongue and lift up the epiglottis. The epiglottis is the flap of the cartilage covering your windpipe that closes during swallowing and opens during breathing. Your doctor may remove small growths or tissue samples for testing (biopsy). They can also use direct laryngoscopy to insert a tube into your windpipe to help you breathe during surgery or in an emergency. With this type of laryngoscopy, you will be given general anesthesia.
How Long Should I Stay in Tokyo for a Laryngoscopy Procedure?
The stay period in Tokyo for a Laryngoscopy can widely differ depending on personal situations. Usually, Laryngoscopy is an outpatient process, suggesting that patients often leave on the same day. Since the results will usually be available within a few days, it is advisable that you stay in Tokyo for 3 to 7 days. Once the results are ready, you will have to visit your doctor to discuss the results. Considering potential follow-up visits that might need a more extended stay is also crucial.
What's the Recovery Time for Laryngoscopy Procedures in Tokyo?
It's crucial to understand that recovery can be quite swift, with many patients able to return to normal activities within a day or two. However, some patients may experience a sore throat, mild discomfort, or hoarseness for a few days after the procedure. Those symptoms can generally be managed with over-the-counter pain medication, rest, and consuming plenty of fluids.
Your throat may be slightly swollen or feel sore for around 2 to 5 days. You may also notice that your voice sounds hoarse. This may resolve within 1 to 8 weeks. You may be asked to speak as little as possible for a week or two. Therefore, if your job requires using your voice, you should take 1 to 2 weeks off work.
What sort of Aftercare is Required for Laryngoscopy Procedures in Tokyo?
Your doctor will give you detailed instructions on what you can and cannot do during your recovery time. Since your mouth and throat will be numb for a couple of hours following the procedure, you will not be allowed to drink or eat anything until the numbness subsides. Your throat may be sore once the numbness wears off. You can gargle with salt water or suck on ice to ease it. Your doctor may also recommend you to take over-the-counter pain relievers.
Keeping an open line of dialogue with your medical practitioner is paramount, informing them of any uncommon symptoms like extended discomfort, trouble with swallowing, or breathing irregularities. Part of your post-treatment care includes routine check-ins, during these sessions, your health provider will track your recovery and deliberate the result of the operation.
What's the Success Rate of Laryngoscopy Procedures in Tokyo?
Recognizing that the Laryngoscopy serves primarily as a diagnostic technique rather than a curative measure is crucial. Usually, its efficacy can be gauged by its capacity to accurately pinpoint disorders impacting the larynx. Broadly speaking, the Laryngoscopy boasts an impressive success rate in accomplishing its chief objective of rendering a comprehensive perspective of the larynx. Nevertheless, the effectiveness of any follow-up treatments hinges on the specific diagnosed condition, the selected therapeutic course, and personal patient factors. In the aspect of detecting cancer, the procedure is hailed for its 100% precision rate.
Are there Alternatives to Laryngoscopy Procedures in Tokyo?
The alternative to laryngoscopy depends on the reason why you need it. Sometimes, your doctor may recommend laryngeal electromyography (laryngeal EMG) as the alternative. With a laryngeal EMG, the muscle activity in the vocal cords and throat are assessed. Another procedure called esophagogram, also called a barium swallow, can also be used. In esophagogram, patients drink a small amount of barium prior to the test and an X-ray is used to see the structure and function of the esophagus during swallowing.
However, these alternatives may not provide the same level of detail or allow for the same diagnostic possibilities as the Laryngoscopy. Thus, the choice of procedure will depend on individual needs and circumstances.
What Should You Expect Before and After the Procedure
Before the process, your medical specialist will carry out a comprehensive health assessment and suggest any needed safety measures. This might include abstaining from food for a certain period ahead of the process to confirm the unobstructed entry for the laryngoscope.
Post-process, there could be a likelihood of a tender throat or a raspy voice for some days, usually mitigated with relaxation and regular medicines. Regular interactions with your medical specialist regarding any concerns or abnormal signs is crucial. A subsequent meeting might be arranged to converse about the results of the process and any impending necessary actions. Hopefully the cause of your symptoms will be found, your problems should be treated, and any foreign object should be removed
What are the Potential Risks of Laryngoscopy?
Generally, Laryngoscopy is considered a safe procedure, but like any medical intervention, it carries a certain degree of risk. It's essential to discuss any potential risks with your healthcare provider to make an informed decision. You should be aware that there are some side effects and risks of laryngoscopy.
These include:
-
Bleeding
-
Pain or swelling in your throat, tongue, or mouth
-
Hoarseness
-
Infection
-
Gagging or vomiting.
What Happens If Abnormalities Are Found During a Laryngoscopy?
Should there be detection of any irregularities like polyps, cysts, or cancer indications during the Laryngoscopy, your medical expert will review the findings and the subsequent measures with you. Based on the circumstances, this might encompass additional examinations such as a biopsy to affirm a diagnosis, or deliberations concerning potential treatment routes.
Though the discovery of unusual characteristics during a Laryngoscopy can evoke worry, it is crucial to bear in mind that prompt detection is critical in successfully tackling many conditions. Keeping an open line of communication with your healthcare authority will aid your comprehension and guide you smoothly through the upcoming stages.
Whilst the information presented here has been accurately sourced and verified by a medical professional for its accuracy, it is still advised to consult with your doctor before pursuing a medical treatment at one of the listed medical providers
No Time?
Tell us what you're looking for and we'll reachout to the top clinics all at once
Enquire Now

Popular Procedures in Tokyo
Prices Start From $111

Prices Start From $973

Prices Start From $759

Prices Start From $231

Recommended Medical Centers in Tokyo for Laryngoscopy

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available
Laryngoscopy in and around Tokyo
About Tokyo
Tokyo is Japan’s capital. It is one of the 47 prefectures of the country. There are over 13.9 million people estimated to live there. The capital is a giant metropolis that offers tourists the chance to indulge in the traditional Japanese culture, eat in one of its delicious restaurants, or learn more about modern life. One of the most popular sights in Tokyo is the cherry blossoms that fill the streets and parks with pink petals in Spring. The soft pink petals are an icon of the country.
Among the 30 million people who traveled to Japan in 2018 are medical tourists. With a vast range of high-quality medical services and facilities, Tokyo has a large contribution to the country’s growing medical tourism. it has numerous public and private hospitals that offer outstanding healthcare. These hospitals are equipped with cutting-edge medical technology and highly qualified doctors. Many doctors and medical professionals speak fluent English.
As Japan was ranked the highest in five-year survival rates of lung cancer and esophagus cancer patients from 2010 to 2014, the most sought-after medical procedure is Tokyo oncology treatments. There are many medical facilities in the area that are JCI-accredited and offers a wide range of treatments including Breast Augmentation procedures.
Popular Areas in Tokyo
Tokyo is sprawling with many extraordinary attractions and sights. It is the perfect mixture of traditional and modern. From temples, shrines, futuristic infrastructure, robot restaurants, booming nightlife, nature to anime, all coexist peacefully here.
To see a beautiful city view, climb up the Tokyo Skytree, Tokyo Metropolitan Government Building, and Tokyo Tower. Visit Tokyo’s oldest temple, Sensoji Temple in Asakusa, and learn more about the history and traditions. The temple is surrounded by numbers of Japanese restaurants that serve authentic dishes including Sushi, Tempura, and Sukiyaki. Tourists can also try a variety of traditional activities like wearing a Kimono dress.
Not far from Asakusa is Ueno, where one of the biggest parks in Tokyo is located. Ueno Park is the perfect place to spend a beautiful day. The park consists of a zoo, museums, historical monument, and green spaces. To try out Tokyo’s futuristic and modern side, come to the first digital art museum in the world, MORI Building DIGITAL ART MUSEUM — teamLab Borderless. Experience a unique interactive art with the latest technology and immerse in multiple digital art exhibitions.
Shopping is also one of the main attractions in Tokyo. Tourists most favorite places to shop are Ginza, Nakamise Shopping Street, as well as Takeshita Street and Omotesando in Harajuku. For anime or Disney fans, attractions such as Ghibli Museum, Fujiko F Fujio Museum, Pokemon Center, Tokyo One Piece Tower, Nakano Broadway, Akihabara, Tokyo Disneyland, and Tokyo Disney Sea are some of the best places to visit.
Weather and Climate in Tokyo
Tokyo is a year-round destination because it has temperate weather with four distinct seasons.
- Summer is hot and humid with an average temperature of 21 to 32 °C. Sometimes it can get as high as 40 °C. this season starts in June and ends in August. June sees a lot of rainfall while August is the start of typhoon season.
- Autumn lasts from September to November. The typhoon season peaks in November. The weather during this season is mild with less humidity. It is pleasantly warm in October, making it one of the best times to travel in Tokyo.
- Winter comes in December and lasts until February. The weather is dry and sunny with an average temperature of around 2 °C to 12 °C. The temperature rarely drops below 0 °C. There is very little snow in Tokyo.
- Spring starts in March to May. The temperature increases gradually during this season, with an average of 13 °C in the afternoon and 5 °C in the morning and evening. The sky is mostly clear during this season and it is also one of the best times to visit Japan because of the cherry blossoms.
Getting Around in Tokyo
Located around 60km east of central Tokyo, Narita International Airport is the main international gateway to Tokyo. The airport serves both domestic and international flights to almost every major city in the world. Budget airlines such as Jetstar Japan, Peach, and Eastar Jet operates flights from this airport.
Rail, bus, taxi, or car rental are available for tourists to reach the city center from Narita Airport. There are several train types to choose from. The Main Line (regular commuter train) in Keisei Line is the most affordable one, it costs around ¥1,190 to ¥1,230 ($10 to $11.3) and it connects with the Toei Asakusa Subway Line and the Yamanote Line. For faster travel, choose the Skyliner train that takes only 36 minutes to Nippori. This train costs around ¥2,470 ($22.7). There is another train known as the Sky Access Express train that offers better access to Tokyo. A trip to Asakusa takes about 58 minutes and costs around ¥1,290 ($11.9).
A taxi might not be the best option since it’s very expensive, it usually costs over ¥20,000 ($184) from Narita Airport to Tokyo. The more affordable option is the shared minibus which cost ¥6,180 ($57) per person. Buses are comfortable, the Limousine Bus costs around ¥2,880 ($26.5) and the Tokyo Shuttle costs around ¥900 ($8) to ¥1,000 ($9).
Tokyo is served by one of the best public transport systems in the world. Trains and subways are the best way to get around the city. It is the cheapest and fastest mode of transportation. Taxis are easily available and can be hailed on the street except in areas like Ginza, where taxis are only allowed to stop in taxi stands. The base fare is ¥430 ($4) for the first 1.5 km and ¥80 ($0.7) for every 237 meters.
Tourist Visas in Tokyo
Japan allows citizens of 68 countries and territories to stay in the country for up to 90 days. Citizens of Indonesia, Brunei, and Thailand are granted a 15-day visa-free trip. The country has a visa for a medical stay that grants long-term stays to medical tourists and approval for visa holders to travel back and forth between their home countries and Japan. Foreign visitors who visit Japan on tourist visas can also receive medical services, except for long-term therapies and surgeries that require more than three months.
Additional Information
- Local Currency: The official currency is the Japanese Yen (¥). There is around ¥111 per $1.
- Money & Payments: ATMs are widely available and can be found in post offices or convenient stores (especially 7-Eleven). Credit cards are accepted in some hotels, restaurants, and shops but it is advisable to always bring cash. Tipping is optional.
- Local Language: Japanese is the official language. Most people speak limited English but many restaurant menus and signs are written in both Japanese and English.
- Local Culture and Religion: The main religion is Shintoism and Buddhism. There is a small group of Christians in the city.
- Public Holidays: There are sixteen major public holidays in Japan. The city hosts annual festivals including Fuji Matsuri, Hinode Matsuri, and Tenno Matsuri.
Popular Searches
- Plastic Surgery in Thailand
- Dental Implants in Thailand
- Hair Transplant in Thailand
- Breast Augmentation Thailand
- Gastric Sleeve in Thailand
- Gender Reassignment Surgery in Thailand
- Laser Hair Removal in Bangkok
- Botox in Bangkok
- Dermatology in Bangkok
- Breast Augmentation in Bangkok
- Coolsculpting in Bangkok
- Veneers in Turkey
- Hair Transplant in Turkey
- Rhinoplasty in Turkey
- Stem Cell Therapy in Mexico
- Rhinoplasty in Mexico
- Liposuction in Mexico
- Coolsculpting in Tijuana
- Rhinoplasty in Korea
- Scar Removal in Korea
- Gastric Sleeve in Turkey
- Bone Marrow Transplant in India
- Invisalign in Malaysia
- Plastic Surgery in the Dominican Republic
- Tummy Tuck in the Dominican Republic
- Plastic and Cosmetic Surgery in Poland
- Rhinoplasty in Poland
- Hair Implant in Poland
- Dental Implants in Poland
- IVF in Turkey
