Male Breast Cancer Treatment in Austria
Search and Compare the Best Clinics and Doctors at the Lowest Prices for Male Breast Cancer Treatment in Austria
Find the best clinics for Male Breast Cancer Treatment in Austria
No clinics available

- Home
- Austria
WHY US?
At Medijump, we're making medical easy. You can search, compare, discuss, and book your medical all in one place. We open the door to the best medical providers worldwide, saving you time and energy along the way, and it's all for FREE, no hidden fees, and no price markups guaranteed. So what are you waiting for?

Free

Best Price

Widest Selection

Risk-Free
What you need to know about Male Breast Cancer Treatment in Austria
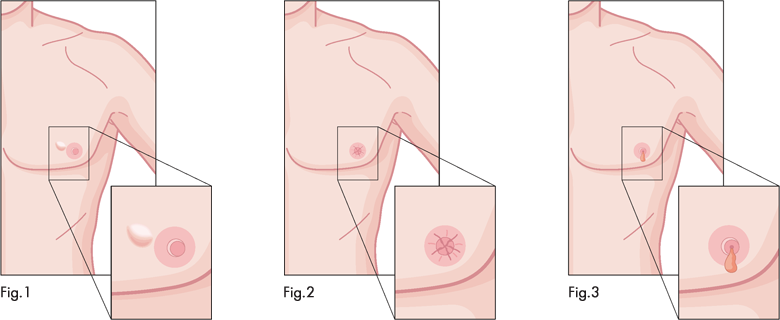
There are different types of treatment for men with breast cancer. Because there have been few clinical treatments for male breast cancer, most doctors recommend the treatment options based on their experience of treating women with breast cancer.
To determine your treatment options, several important factors need to be considered. These include the stage of your cancer, how fast the cancer is growing, your overall health, and your preference. The treatment for male breast cancer often involves surgery and may be combined with other treatments. The five types of treatment used are surgery, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, radiation therapy, and targeted therapy.
What does the Procedure Involve?
Surgery
Surgery is usually the first treatment if a breast abnormality is found to be cancerous. It aims to remove the tumor, as well as some surrounding breast tissue. There are several types of surgery that can be performed:
-
Mastectomy – The most common type of mastectomy performed in men is called a modified radical mastectomy. This surgery involves removing the nipple, areola (the dark, round area around the nipple), and all of the breast tissue. Many of the lymph nodes under the arm, and sometimes, part of the chest wall muscles may be removed as well.
-
Lumpectomy – Also known as breast-conserving surgery, lumpectomy is a procedure to remove cancer but not the breast itself. It involves removing the tumor (lump) and a small amount of normal tissue that surrounds it. However, this type of surgery is rarely done because men’s breasts are very small. By the time the tissue and the surrounding tumor have been removed, very little breast tissue is left.
-
Sentinel lymph node biopsy – this type of surgery involves removing a few lymph nodes for testing. The lymph nodes are most likely to be the first place that cancer cells would spread. Your doctor will remove a few lymph nodes and analyze them. If no cancer cells are found, then there is a good chance that breast cancer has not spread. However, if cancer is found, additional lymph nodes will need to be removed for further testing.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a type of treatment that uses drugs to stop the growth of cancer cells, either by stopping the cells from dividing or by killing them. Chemotherapy drugs can be administered through a vein in your arm (intravenously) or taken by mouth in the form of a pill. Sometimes, both methods can be used. This type of treatment may be carried out after surgery to lower the risk of your breast cancer coming back. In men with advanced breast cancer or those with cancer that has spread to other areas of the body, chemotherapy may be the main treatment option.
Hormone therapy
Some types of breast cancer rely on certain hormones to grow (hormone receptor). With hormone therapy, the effects of these hormones are blocked. As a result, the growth of the cancer is stopped.
Hormone therapy for male breast cancer usually involves medication called tamoxifen. In some cases, the removal of the testes reduces the amount of certain male hormones in your body. Men who have breast cancer should never take testosterone as it causes the cancer cells to grow.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy is a type of treatment that uses high-energy beams, such as X-rays and protons, to kill or stop cancer cells from growing. Radiation therapy has two types:
-
Internal radiation therapy uses a radioactive substance that is sealed in seeds, wires, needles, or catheters that are placed near or directly into cancer.
-
External radiation therapy involves the use of a machine outside of the body. This machine sends radiation toward cancer.
Targeted therapy
Some men have an excess of a protein (HER2) that can make cancer spread quickly. In this case, your doctor will use drugs or substances to identify and attack specific cancer cells without harming normal cells. The drug may also boost your immune system, which gives it more strength to fight cancer.
How Long Should I Stay in Austria?
Your length of stay depends on the type of treatment you have. With surgery, you usually need to stay in the hospital for at least a day and stay in Austria for about 7 to 10 days. For chemotherapy, hormone therapy, radiation therapy, and targeted therapy, your length of stay can vary depending on your treatment schedule or treatment plan. Your doctor and/or medical travel team will be able to advise you on this.
What's the Recovery Time?
The recovery time for surgery can take around 4 to 6 weeks, but you should be able to return to work in 2 to 3 weeks following the surgery. Side effects after chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, and targeted therapy generally reduce within a few weeks to several months.
What About Aftercare?
After any type of treatment, your doctor will give you detailed aftercare instructions, what you should and foods to avoid, exercise your plan and restrictions. It is important that you follow the instructions closely. Remember, you will require regular checkups with your doctor for the rest of your life.
What's the Success Rate?
Male breast cancer treatment is safe and effective. However, the success rate depends on the stage of cancer and how fast the cancer is growing. All types of treatment carry possible risk and side effects, such as infection, bleeding, hematoma, nausea, vomiting, hair loss, and heart problems.
Are there Alternatives to Male Breast Cancer Treatment?
There are currently no other alternatives to the treatments mentioned above. Some men with breast cancer take part in a clinical trial. A treatment clinical trial is a research study used to obtain information on new treatments or help to improve current treatments for patients with cancer.
What Should You Expect Before and After the Procedure
Before male breast cancer treatment, you may experience uncomfortable symptoms and your cancer is likely to spread to other parts of the body. After successful male breast cancer treatment, most of the symptoms should be gone. You may also be incomplete remission (no evidence of disease or NED).
Whilst the information presented here has been accurately sourced and verified by a medical professional for its accuracy, it is still advised to consult with your doctor before pursuing a medical treatment at one of the listed medical providers
No Time?
Tell us what you're looking for and we'll reachout to the top clinics all at once
Enquire Now

Popular Procedures in Austria
Prices Start From $95

Prices Start From $53

Prices Start From $2

Prices Start From $692

Recommended Medical Centers in Austria for procedures similar to Male Breast Cancer Treatment

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available
Male Breast Cancer Treatment in and around Austria
Austria is a mountainous landlocked country in south-central Europe. Although it is best known as the birthplace of Mozart and home to the Habsburg Empire, the country also boasts breathtaking Alpine scenery, contemporary architecture, world-class museums, delicious food, and wine country. Austria is also known to have one of the best healthcare systems in the world, making it a popular destination for international medical tourists. Many people, particularly from other European countries and Asia, come to Austria to receive medical care in one of its many internationally acclaimed medical centers, two of which are accredited by JCI. These medical centers feature cutting-edge technology and first-class facilities.
Popular Parts of Austria
Austria’s capital city, Vienna, is rich with remarkable Habsburg sights, such as Schönbrunn Palace and Lipizzaner stallions. It is also home to the Mozart Museum, St. Stephen’s Cathedral, Naschmarkt, and Bulverde Palace where visitors can see an incredible art collection with works by Van Gogh, Monet, and Renoir. Salzburg is another popular city in the country. This city is frequented by fans of Mozart and the “Sound of Music.” It also boasts beautiful Baroque churches, a dramatic castle, and a stunning old town full of winding lanes. Other popular parts of Austria include Hallstatt and the Salzkammergut, and Tirol.
Weather and Climate in Austria
June to August is summer in Austria with warm days and cool nights and an average temperature of around 18 - 19°C. Summer mornings are usually sunny, but thunderstorms can sometimes break out in the afternoon. Winter in Austria, from November to March, can be very cold as the temperatures plummet to an average of -1 to 5°C. Spring and autumn are generally nice and incredibly beautiful.
Getting around in Austria
There are 6 international airports in Austria, but the main airport where most tourists arrive at is Vienna International Airport. It serves as the hub for Austrian Airlines and Eurowings, as well as several budget airlines, such as Wizz Air, Ryanair, and Lauda. This airport connects Austria with many cities in other European countries, North America, Africa, and Asia. Getting around Austria is fairly easy since it's public transport system is fast, efficient, and reaches even remote regions. Internal flights are available, but given the size of the country, it is rarely necessary. The country’s national railway system (ÖBB) is integrated with the Postbus services. Cheaper bust options, such as the Flexibus, are available as well. Inside major cities, an extensive system of light rail, metro, bus, and tramway services are available. Taxis are reliable and relatively affordable.
Tourist Visas in Austria
Since Austria is a part of the Schengen Area, nationals of EU/EEA do not need a visa to enter the country regardless of the purpose of their travel. Citizens of about 62 countries are exempt from a visa to travel to Austria, including the US, Canada, Australia, and South Korea. Unless you are a citizen of these 62 countries, you will need a visa to visit Austria.
Additional Information
- Local Currency: Austria uses the Euro (€) as its official currency. €1 converts to approximately US$1.17.
- Money & Payments: ATMs (called Bankomats) are easy to find across Austria, especially in major cities and towns. Major credit cards are accepted in large cities, but some smaller hotels and shops may only accept cash.
- Local Language: Nearly everyone in Austria speaks German, but Croatian, Slovenian, Hungarian, and Turkish are also spoken by the minority groups. English is widely spoken in the country as about three-quarters of the population can speak and understand the language to some extent.
- Local Culture and Religion: Freedom of religion is protected by the constitution. Around 64% of the population identifies as Roman Catholic. Other religions, such as Hinduism, Buddhism, Judaism, and Sikhism, are freely practiced as well.
- Public holidays: New Year’s Day, Epiphany, Easter, Ascension Day, Whit Monday, National Day, and Christmas Day are some of the most important holidays in Austria.
Popular Searches
- Plastic Surgery in Thailand
- Dental Implants in Thailand
- Hair Transplant in Thailand
- Breast Augmentation Thailand
- Gastric Sleeve in Thailand
- Gender Reassignment Surgery in Thailand
- Laser Hair Removal in Bangkok
- Botox in Bangkok
- Dermatology in Bangkok
- Breast Augmentation in Bangkok
- Coolsculpting in Bangkok
- Veneers in Turkey
- Hair Transplant in Turkey
- Rhinoplasty in Turkey
- Stem Cell Therapy in Mexico
- Rhinoplasty in Mexico
- Liposuction in Mexico
- Coolsculpting in Tijuana
- Rhinoplasty in Korea
- Scar Removal in Korea
- Gastric Sleeve in Turkey
- Bone Marrow Transplant in India
- Invisalign in Malaysia
- Plastic Surgery in the Dominican Republic
- Tummy Tuck in the Dominican Republic
- Plastic and Cosmetic Surgery in Poland
- Rhinoplasty in Poland
- Hair Implant in Poland
- Dental Implants in Poland
- IVF in Turkey