Chemotherapy in Japan
Search and Compare the Best Clinics and Doctors at the Lowest Prices for Chemotherapy in Japan
Find the best clinics for Chemotherapy in Japan
No pricing info available
Morocco offers the best prices Worldwide
Price: $ 114
From 94 verified reviews
Hisanori Kakuma, 16 September 2020
Thank you for all the help you have given me
The University Hospital of Tokyo, located in Chome Yushima, Tokyo, Japan offers patients Chemotherapy procedures among its total of 286 available procedures, across 30 different specialties. Currently, there's no pricing information for Chemotherapy procedures at The University Hospital of Tokyo, as all prices are available on request only. There is currently a lack of information available on the specialists practicing at the Hospital, and they are not accredited by any recognized accreditations institutes
- Home
- Japan
WHY US?
At Medijump, we're making medical easy. You can search, compare, discuss, and book your medical all in one place. We open the door to the best medical providers worldwide, saving you time and energy along the way, and it's all for FREE, no hidden fees, and no price markups guaranteed. So what are you waiting for?

Free

Best Price

Widest Selection

Risk-Free
What you need to know about Chemotherapy in Japan
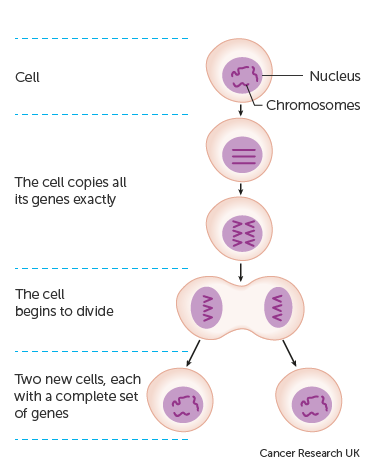
Chemotherapy is a type of treatment where medicine with powerful chemicals is used to destroy fast-growing cells in the body. It is usually used to treat cancer because cancer cells can grow and multiply faster than most other cells within the body. While it is not a singularly defined service, it generally involves a series of treatments administered in cycles over a period of weeks or months, with rest periods in between.
Chemotherapy may be used in a variety of settings for people with cancer, including:
-
As the primary treatment for cancer (alone without other types of treatments).
-
In combination with other therapies, such as radiation, surgery, or hormone therapy.
-
After other types of cancer treatments, such as surgery, to kill hidden cancer cells that may remain in the body. This is called adjuvant therapy.
-
To prepare your body for other treatments, such as surgery and radiation, by shrinking a tumor. This is called neoadjuvant therapy.
-
To help relieve symptoms of cancer by destroying some of the cancer cells. This is called palliative chemotherapy.
Besides treating cancer, some chemotherapy drugs can be used to treat other conditions, such as immune system disorders and bone marrow diseases.
What is the cost of Chemotherapy in Japan?
The expense of Chemotherapy in Japan can fluctuate significantly due to various elements. These elements include the cancer type and its stage, the particular chemotherapy medications employed, the schedule and length of procedures, as well as the fees charged by the healthcare provider. Extra expenses arising from the procedure - like diagnostic examinations, hospitalizations, and post-procedure care - must also be taken into account.
Although determining an accurate expense without a detailed treatment plan might be tough, it's essential to engage in a financial discussion with your healthcare professional or a finance expert at the clinic. They are equipped to provide a tentative cost summary, discuss various payment alternatives, and explore possible avenues for financial aid.
What does the Procedure Involve?
Chemotherapy drugs can be given in several different ways. The specific drugs used, their combinations, and the method of administration can vary greatly depending on the type of cancer, its stage, the patient's overall health, and the intended goal of treatment. These include:
-
Chemotherapy infusions – chemotherapy is most commonly given intravenously, which means as an infusion into a vein.
-
Chemotherapy shots – the drugs can be delivered through an injection with a needle to your arm, thigh, or hip, or sometimes in the fatty part of your stomach, leg, or arm.
-
Chemotherapy pills – some types of chemotherapy drugs can be taken orally in a form of pill or capsule that you swallow.
-
Chemotherapy creams – creams or gels that contain chemotherapy drugs can be applied to your skin. This is usually used to treat certain types of skin cancer.
-
Chemotherapy used to treat an area of the body – the drugs can be delivered directly to a specific area of the body. For example, the drugs may be given in your central nervous system (intrathecal chemotherapy), in your abdomen (intraperitoneal chemotherapy), or in your chest cavity (intrapleural chemotherapy).
Chemotherapy delivered directly to the cancer – in some cases, chemotherapy drugs may be given directly to cancer or the location where cancer once was (after surgery).
How Long Should I Stay in Japan?
Chemotherapy is usually given at regular intervals (cycles), meaning a period of treatment and then a period of rest. For instance, a 4-week cycle may include 1 week of treatment and then 3 weeks of rest to allow your normal cells to recover from the drug side effects. In some cases, the doses may be given in a certain number of days in a row or every other day for several days. Some drugs may also be delivered continuously over a set number of days.
Your chemotherapy cycle will be customized depending on your individual case. Therefore, your length of stay in Japan will depend on the schedule/cycle of your chemotherapy. Your doctor and medical travel team will be able to advise you on this matter.
What's the Recovery Time for Chemotherapy Procedures?
The recovery time for Chemotherapy can vary widely depending on the specific type of chemotherapy, the overall health of the patient, and the individual's response to treatment. Some people might feel well enough to return to their normal activities right away, while others may need weeks or months to recover. It is best that you ask your employer if you can work fewer hours, work from home, or adjust your schedule when you have cancer treatment.
It's important to understand that the side effects of chemotherapy can be considerable, and managing these effects is an essential part of the recovery process. Side effects can include fatigue, nausea, hair loss, and an increased risk of infection, among others.
What sort of Aftercare is Required for Chemotherapy Procedures?
Post-treatment care for Chemotherapy involves managing potential side effects and being vigilant for signs of complications or recurrence. Depending on your specific situation, this could translate into regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare professional, blood examinations, imaging tests, or even additional treatments. All this is vital to allow your doctor to evaluate the effectiveness of your treatment.
Self-care is paramount during this period. You should consider the following:
-
Eat food with enough protein and calories to keep your weight up.
-
Wear a hat and use sunscreen SPF 30 or higher when you are out in the sun.
-
Each time you use the toilet, close the lid when flushing and flush twice.
-
Do not have any sexual activity for 48 hours following chemotherapy.
What's the Success Rate of Chemotherapy Procedures?
The efficacy of chemotherapy hinges on a myriad of factors that include the site, nature, and progression phase of your cancer. Your age, general health condition, and any pre-existing health issues also contribute to the success of the procedure. In certain cases, the Chemotherapy can be remarkably successful in eradicating cancer. Some patients may find it helpful for alleviating symptoms, stalling disease progress, and boosting their life quality.
Are there Alternatives to Chemotherapy?
If chemotherapy proves ineffective, or if you're reluctant to proceed with the procedure, your physician may suggest alternative methods such as radiation therapy, immunotherapy, hormone therapy, and targeted therapy. Each of these treatments can function as a standalone or adjunctive treatment.
It's imperative to discuss over all potential treatment paths with your doctor, weighing the prospective advantages, risks, and side-effects of each. In-depth research and clear dialogue with your healthcare provider will help you to make a well-informed choice about the most suitable treatment strategy for your circumstance.
What Should You Expect Before and After the Procedure
Before chemotherapy, your cancer may be dangerous and life-threatening. After successful chemotherapy, your cancer and all of the symptoms should be gone. You should be able to go back to your high quality of life again. However, the response after chemotherapy can be different for each person. For some people, all of the tumor or cancer may disappear, while in others, cancer may have shrunk by a percentage but the disease still remains. There is also a chance that cancer has neither shrunk nor grown.
Can Chemotherapy Be Combined with Other Cancer Treatments?
Chemotherapy is commonly used with other treatments like surgery, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, or targeted therapies. The mix of treatments chosen depends on factors such as the nature and progression stage of the cancer, the patient's wellbeing, and the specific objectives of the treatment.
Pairing Chemotherapy with other treatments could enhance the potency of cancer treatment by combating cancer via various methods. Nonetheless, this could also elevate the risk of side effects. It's vital to engage in discussions about the potential advantages, hazards, and side effects of any multi-treatment approach with your healthcare provider.
What are Potential Risks associated with Chemotherapy?
It is key to remember that chemotherapy comes with a range of side effects, including dryness in the mouth, diarrhea, oral ulcers, fever, hair loss, tiredness, decreased appetite, weight loss, and more. There's also the potential for sustained effects, which could inflict damage to the kidneys, heart, lungs, reproductive system, and nervous system.
Whilst the information presented here has been accurately sourced and verified by a medical professional for its accuracy, it is still advised to consult with your doctor before pursuing a medical treatment at one of the listed medical providers
No Time?
Tell us what you're looking for and we'll reachout to the top clinics all at once
Enquire Now

Popular Procedures in Japan
Prices Start From $39

Prices Start From $95

Prices Start From $53

Prices Start From $2,487

Recommended Medical Centers in Japan for Chemotherapy

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available
Chemotherapy in and around Japan
About Japan
Japan is special in its own way; the culture, food, people, as well as technology are envied by the world over. With old Japan, comes the ancient tradition in the form of a geisha performance, onsen (hot spring) visit in the mountains, tea ceremony, or shrine visit. In contrast, there is modern Japan, full of smart systems and electronics, colorful advertisements and displays, and ultra-modern architecture. In recent years, Japan has become one of the top destinations in the world for oncology treatments and sees many tens of thousands of medical tourists each year. Many of these travel from within the region, including China and Korea, but they are unable to compete with the SE Asian nations with prices. Private hospitals are located across the country, with a particular focus in major cities like Tokyo, Kyoto, and Osaka. 25 of these facilities are JCI-accredited, with many offering Chemotherapy procedures.
Popular Parts of Japan
Located in the Pacific Ocean, Japan is a stratovolcano archipelago. The four largest islands are Honshu, Hokkaido, Kyushu, and Shikoku. With a population of 127 million, 98% are ethnic Japanese. The country perfectly balances traditional with modern technology. Tourists will first see its exceptionally modern face, but after traveling around, they will find many opportunities to connect with the beautiful traditional culture.
- Tokyo is Japan’s capital, one of the 47 prefectures of Japan. It’s a huge metropolis that offers traditional arts and culture, futuristic infrastructures, and good restaurants. The cherry blossoms that bloom in Spring is one of the most popular sights. The soft pink petals are an icon of the country. There is an unlimited choice of shopping, many museums that cover every era of Japanese art history, and even a robot restaurant.
- Kyoto is made of religious architecture, with around 2000 temples and shrines. It moves at a slower pace than any other city in Japan. Filled with samurais, geishas, Zen gardens, and the torii gate, Kyoto is the spiritual center of Japan. The city is also known for its food, head to the Nishiki Market, a four-hundred-year-old local food market that offers a range of national cuisine to modern food from all over the world.
- Osaka, the second largest metropolitan area after Tokyo is known to be the most delicious city. The city is nicknamed “the nation’s kitchen.” Visit Dotonburi to experience the food culture of Osaka. Besides the food, there are numerous attractions that tourists should visit such as Universal Studios Japan, Cup Noodles Museum, Aquarium Kaiyukan, Osaka Castle, and Umeda Sky Building.
- Fukuoka has a welcoming feel with sunny weather and so much to do. It’s made up of two towns, the port city of Hakata and the former castle town of Fukuoka. Visit the impressive Fukuoka Castle, explore the Sumiyoshi-Jinja Shrine, learn history in Kyūshū National Museum, experience the ancient art of calligraphy and origami in Hakata Machiya Folk Museum, and enjoy a calming bath in one of the Onsen hot springs.
- Nagoya is the industrial center of Japan. It’s the birthplace of Toyota and a popular pinball-style game Pachinko. Although many of the historic buildings were destroyed in the air raids of 1945, tourists can still indulge in its culture and tradition. Visit the Nagoya Castle that was reconstructed in 1959, walk around the Atsuta Shrine, or see the history of the automobile in the Toyota Automobile Museum.
Weather and Climate in Japan
Japan has four distinct seasons.
- Summer starts in June and lasts until August. The temperature can get very hot, up to 40 °C in some places, with high humidity. June is the rainy season where the farmers plant their rice. The rainy season is over in August but the typhoon season starts to peak.
- Autumn starts in September and ends in November. September has the greatest risk of typhoons. The weather is generally mild. October is pleasantly warm with less humidity than in summer, making it a food time for traveling the country.
- The temperature will drop in Winter. It lasts from December to February and is usually dry, pleasant, and sunny. The average temperature is around 2°C to 12°C, it rarely drops below 0°C. The northern island of Hokkaido, the Japan Alps, and the Japan Sea coast get a lot of snow while Tokyo gets very little snow.
- Spring is said to be the best time to visit Japan because of its mild weather and cherry blossoms. The season starts in March and ends in May. The temperature will gradually increase during spring with little rainfall and clear sky.
Getting Around in Japan
The main airport for international tourists is the Narita International Airport. It is located around 60km east of central Tokyo. It serves both domestic and international flights to almost every major city around the globe. There are several budget airlines that operate flights from this airport, namely Jetstar Japan, Eastar Jet, and Peach. There are other international airports such as Kansai International Airport, New Chitose International Airport, and Kyushu Saga International Airport.
To get to Tokyo from Narita Airport, tourists can use the rail, bus, taxi, or car rental. The most affordable train line is the Keisei Line that connects with the Toei Asakusa Subway Line and the Yamanote Line, it costs around ¥1,190 to ¥1,230 ($10 to $11.3). There’s also the Sky Access Express train that offers better access to Tokyo, a trip to Asakusa will cost around ¥1,290 ($11.9) and take about 58 minutes. The quickest way to get to Tokyo will be by the Skyliner train, it takes just 36 minutes to Nippori and will cost around ¥2,470 ($22.7). The airport introduced N’EX Tokyo Round-Trip ticket for foreign passport holders that provides round-trip travel from Narita to Tokyo and back for ¥4,000 ($37) for adults and ¥2,000 ($18.4) for children.
A regular taxi from Narita to Tokyo is very expensive, usually over ¥20,000 ($184). The best option is the shared minibus that starts with ¥6,180 ($57) per person. Buses are usually more affordable, the Limousine Bus costs ¥2,880 ($26.5) and the Tokyo Shuttle costs around ¥900 ($8) to ¥1,000 ($9).
Getting around Japan is fairly easy because the country has excellent public transportation. It is recommended to get a Japan Rail Pass. Japan’s bullet train is fast but expensive. There are cheaper train options. Buses are less expensive but will take more time than trains.
Tourist Visas in Japan
Citizens of 68 countries and territories can enter and stay in Japan for up to 90 days without a visa. Citizens of Indonesia, Brunei, and Thailand are granted a 15-day visa-free trip to Japan. Citizens of the United Arab Emirates are allowed to stay for 30 days without a visa. It is advisable to contact the nearest Consular Section of the Embassy or Consulate General of Japan for more information.
Additional Information
- Local Currency: Yen (¥) is the local currency. $1 will get you ¥11 ¥1,000 is worth approximately $9.
- Money & Payments: ATMs are usually located in post offices and convenient stores. There are only a few branches of major Japanese banks that accept foreign-issued cards. Credit cards are accepted in major cities, but the rural area doesn’t. It’s best to always bring cash and bring a coin purse because everything below ¥500 is coins. Tipping is not mandatory, high-end hotels and restaurants usually add a 10% service fee to the bill.
- Local Language: The official language is Japanese. English is common in major cities with many tourists such as Tokyo, Osaka, and Tokyo. Some restaurants write their menu in English and Japanese.
- Local Culture and Religion: The dominant religion in Japan is Shinto and Buddhism. There’s a small group of Christians as well.
- Public Holidays: Japan has sixteen national holidays each year, including Children’s Day, Constitution Memorial Day, and Marine Day. The country hosts numerous annual festivals such as Gion Matsuri in Kyoto, Awa Odori in Tokushima, and Yuki Matsuri Snow Festival in Sapporo.
Popular Searches
- Plastic Surgery in Thailand
- Dental Implants in Thailand
- Hair Transplant in Thailand
- Breast Augmentation Thailand
- Gastric Sleeve in Thailand
- Gender Reassignment Surgery in Thailand
- Laser Hair Removal in Bangkok
- Botox in Bangkok
- Dermatology in Bangkok
- Breast Augmentation in Bangkok
- Coolsculpting in Bangkok
- Veneers in Turkey
- Hair Transplant in Turkey
- Rhinoplasty in Turkey
- Stem Cell Therapy in Mexico
- Rhinoplasty in Mexico
- Liposuction in Mexico
- Coolsculpting in Tijuana
- Rhinoplasty in Korea
- Scar Removal in Korea
- Gastric Sleeve in Turkey
- Bone Marrow Transplant in India
- Invisalign in Malaysia
- Plastic Surgery in the Dominican Republic
- Tummy Tuck in the Dominican Republic
- Plastic and Cosmetic Surgery in Poland
- Rhinoplasty in Poland
- Hair Implant in Poland
- Dental Implants in Poland
- IVF in Turkey

