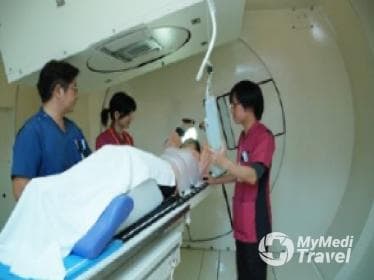
Oncology in Japan
Find the best clinics for Oncology in Japan
With Medijump you can browse 3 facilities offering 3 different types of Oncology procedures in Japan.
From 94 verified reviews
Hisanori Kakuma, 16 September 2020
Thank you for all the help you have given me
Medipolis Proton Therapy and Research Center, located in Kagoshima ken, Ibusuki, Japan offers patients Oncology Consultation procedures among its total of 4 available procedures, across 1 different specialties. Currently, there's no pricing information for Oncology Consultation procedures at Medipolis Proton Therapy and Research Center, as all prices are available on request only. There is currently a lack of information available on the specialists practicing at the Clinic, and they are not accredited by any recognized accreditations institutes
The University Hospital of Tokyo, located in Chome Yushima, Tokyo, Japan offers patients Vaginal Cancer Treatment procedures among its total of 286 available procedures, across 30 different specialties. Currently, there's no pricing information for Vaginal Cancer Treatment procedures at The University Hospital of Tokyo, as all prices are available on request only. There is currently a lack of information available on the specialists practicing at the Hospital, and they are not accredited by any recognized accreditations institutes
- Home
- Japan
WHY US?
At Medijump, we're making medical easy. You can search, compare, discuss, and book your medical all in one place. We open the door to the best medical providers worldwide, saving you time and energy along the way, and it's all for FREE, no hidden fees, and no price markups guaranteed. So what are you waiting for?

Free

Best Price

Widest Selection

Risk-Free
Oncology is the branch of medicine that focuses on the research, prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of cancer. A medical professional who specializes in diagnosing and treating people with cancer is called an oncologist.
An oncologist can design a treatment plan based on detailed pathology reports that shows the type of cancer the patient has, how much cancer has developed, how fast the cancer is likely to spread, and what parts of the patient's body are involved.
The field of oncology has three main areas, which include:
- Medical oncologists use chemotherapy, hormonal therapies, and other types of targeted treatments to treat cancer. Most people think of medical oncologist as their primary cancer doctor. Medical oncologists help monitor and maintain patients' well-being, as well as helping patients manage side effects. Often patients follow up with their medical oncologist once their treatment is complete.
- Surgical oncologists perform the surgical removal of the tumor and surrounding tissue. They will help patients prepare for and recover from any surgical procedure they undergo during their cancer treatment. If your primary doctor suspects that you have cancer, a surgical oncologist is likely one of the first doctors you see. Surgical oncologists can perform biopsies, which involves removing a small tissue sample to be checked for cancer cells.
- Radiation oncologists treat cancer using radiation therapy. They use high-energy photon beams to target and destroy cancer cells. Approximately one-half of all cancer patients will undergo radiation treatment during their cancer care.
Because most cancers are treated with a combination of therapies, you could see two or all three different oncologists during the course of your treatment.
Besides the three main areas, there are also several other areas of oncology. These include:
- Pediatric oncologists diagnose and treat cancer in children. Some types of cancer appear more often in children and teenagers, such as leukemia, brain tumors, osteosarcoma, and Ewing’s sarcoma. Some pediatric oncologists focus on conducting research on childhood cancers, while others specialize in certain types of cancer.
- Gynecologic oncologists treat cancers that affect women, such as cancer of the ovary, cervix, uterus, vagina, and vulva. Additionally, they also treat complicated gynecological conditions that are not cancerous, such as fibroid tumors and endometriosis.
- Hematologist-oncologists diagnoses and treats blood cancers, such as lymphoma, leukemia, and myeloma. They may also specialize in the management of solid tumors.
Oncologists usually work with a variety of other medical professionals, including pathologists, diagnostic radiologists, oncology nurses, and oncology social workers. They may also work with doctors from other areas of medicine, such as neurologists, dermatologists, or urologists.
What does Oncology Involve?
There are many types of procedures to treat cancer. The types of procedures that you receive will depend on the type of cancer you have and how advanced it is. Some people who have cancer will only have one treatment. However, most people have a combination of treatments, such as surgery with radiation therapy and/or chemotherapy. Below are the types of procedures to treat cancer:
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is a type of treatment that uses drugs to kill cancer cells in the body and prevent them from growing. The drugs can prevent cell division, target the food source of the cancer cells’ (the hormones and enzymes the cells need to grow), and trigger apoptosis (a process in which cancer cells kill themselves).
- Chemotherapy drugs can be given in several different ways, including.
- Oral – taken in a pill or capsule form.
- Intravenously – through an infusion into a vein.
- Shots – injected with a needle.
- Topical – applying creams or gels into the skin. This type is used to treat certain types of skin cancer.
Chemotherapy drugs can also be given directly to cancer or directly to an area of the body, such as the abdomen or central nervous system.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy, or biologic therapy, boosts your body’s natural defenses to fight cancer. It uses substances made by your own body, or in a laboratory, to improve or restore your immune system function. It can stop cancer from spreading to other parts of the body, stop or slow the growth of cancer cells, and help your immune system work better at destroying cancer cells.
There are several types of immunotherapy to treat cancer, including immune checkpoint inhibitors, T-cell transfer therapy, monoclonal antibodies, treatment vaccines, and immune system modulators. Different types of immunotherapy may be given in different ways, such as intravenous (IV), oral, intravesical (directly into the bladder), or topical.
Targeted therapy
Targeted therapy uses drugs that are designed to specifically “target” cancer cells without affecting normal cells. It targets the cancer’s specific proteins, genes, or other tissue environment contributing to cancer survival and growth. These proteins and genes are found in cancer cells or in cells related to cancer growth.
The targeted drugs can block or turn off chemical signals that tell cancer cells when to divide and grow, stop making new blood vessels that feed cancer cells, change proteins within the cancer cells so the cells die, trigger the immune system to kill cancer cells, and carry toxins in the cancer cells to kill them.
- There are two types of targeted therapy:
- Small-molecule drugs, which is given through pills or capsules that you swallow
- Monoclonal antibodies, which are given through a needle in a blood vein.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses intense energy beams to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors. It most often uses X-rays, but other types of energy, such as protons may also be used.
Radiation therapy can be done in two ways:
- External-beam radiation therapy – this type of radiation therapy delivers radiation from a machine outside the body. You will lie on a table, and the machine (called a linear accelerator) moves around you to deliver radiation from several different angles. It is a quick and painless procedure.
- Internal radiation therapy – also called brachytherapy, involves both temporary and permanent placement of radioactive sources in the body. During the placement of the radioactive sources, you will be given anesthesia.
Hormone therapy
Hormone therapy stops or slows the growth of cancer that uses hormones to grow. It works by blocking your body’s ability to produce hormones or interfere with how hormones behave in your body. It can reduce the chance that cancer will return by stopping or slowing its growth, as well as preventing or reducing symptoms in men with prostate cancer.
Hormone therapy is usually used to treat breast and prostate cancer. It can be taken in many ways, including orally, through an injection, and surgery.
Stem Cell Transplant
People whose blood-forming stem cells are damaged by the very high doses of radiation therapy or chemotherapy can undergo stem cell transplant to restore the cells. Blood-forming stem cells are vital since they grow into different types of blood cells that you need to be healthy. The stem cells will be given to you through an IV catheter. The process is very much like receiving a blood transfusion.
Surgical treatment
Surgical treatment for cancer is a procedure to remove cancer from your body. There are many types of surgeries to treat cancer, which differ based on the part of the body that requires surgery, the purpose of the surgery, the amount of tissue to be removed, and your preference. In general, the surgery can be open or minimally invasive.
- During open surgery, one large incision is made to remove the tumor, some healthy tissue, and some nearby lymph nodes.
- During minimally invasive surgery, a few tiny incisions are made instead of a large one. These incisions are made to insert a laparoscope (a long, thin tube with a camera on its end) and special surgical tools. The laparoscope allows your surgeon to see the inside of the body, and the surgical tools are used to remove the tumor and some healthy tissue.
How Long Should I Stay in Japan?
For chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, hormone therapy, and targeted therapy, the treatment schedule may vary. You may have treatment every day, week, or month. It may also be given in a cycle, which is a period of treatment followed by a period of rest to give your body a chance to recover. For surgical treatment, you may need to stay in the hospital for a few days, and you need to stay in Japan for at least 10 to 14 days. Your oncologist and/or medical tourism team will advise you on the length of stay in Japan.
What's the Recovery Time?
The type of procedure you undergo determines the recovery period. While you may be able to get back to your normal routine within 10 days after laparoscopic surgery, you may need to wait around 6 weeks to fully recover from open surgery. Your oncologist will give you a detailed recovery timeline.
What About Aftercare?
You will be given instructions on how to take care of yourself. Your surgeon or nurse will explain how to control your pain, how to take care of your wound, activities you can and cannot do, and how to spot signs of infections. You may also need to talk to a dietitian to help with eating problems caused by the treatment. You will need to attend follow-up checkups to monitor your condition.
What's the Success Rate?
Cancer survival has improved significantly due to constant advancement and improvements in the field of oncology, including improvement in treatments and screening (allowing for earlier diagnosis). Still, you need to be aware of the risks, such as infection, bleeding, nerve damage, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, and hair loss.
Are there Alternatives to Oncology?
There is no other alternative than to see an oncologist when it comes to cancer treatments. Some people may choose to undergo meditation, hypnosis, and acupuncture as well, usually to relieve the stress, anxiety, and pain that cancer can bring.
Whilst the information presented here has been accurately sourced and verified by a medical professional for its accuracy, it is still advised to consult with your doctor before pursuing a medical treatment at one of the listed medical providers
No Time?
Tell us what you're looking for and we'll reachout to the top clinics all at once
Enquire Now

Popular Procedures in Japan
Price on Request

Prices Start From $1,706

Prices Start From $11

Price on Request

Recommended Medical Centers in Japan for Oncology

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available

- Interpreter services
- Translation service
- Religious facilities
- Medical records transfer
- Medical travel insurance
- Health insurance coordination
- TV in the room
- Safe in the room
- Phone in the room
- Private rooms for patients available
Oncology in and around Japan
About Japan
Japan is special in its own way; the culture, food, people, as well as technology are envied by the world over. With old Japan, comes the ancient tradition in the form of a geisha performance, onsen (hot spring) visit in the mountains, tea ceremony, or shrine visit. In contrast, there is modern Japan, full of smart systems and electronics, colorful advertisements and displays, and ultra-modern architecture. In recent years, Japan has become one of the top destinations in the world for oncology treatments and sees many tens of thousands of medical tourists each year. Many of these travel from within the region, including China and Korea, but they are unable to compete with the SE Asian nations with prices. Private hospitals are located across the country, with a particular focus in major cities like Tokyo, Kyoto, and Osaka. 25 of these facilities are JCI-accredited, with many offering Oncology procedures.
Popular Parts of Japan
Located in the Pacific Ocean, Japan is a stratovolcano archipelago. The four largest islands are Honshu, Hokkaido, Kyushu, and Shikoku. With a population of 127 million, 98% are ethnic Japanese. The country perfectly balances traditional with modern technology. Tourists will first see its exceptionally modern face, but after traveling around, they will find many opportunities to connect with the beautiful traditional culture.
- Tokyo is Japan’s capital, one of the 47 prefectures of Japan. It’s a huge metropolis that offers traditional arts and culture, futuristic infrastructures, and good restaurants. The cherry blossoms that bloom in Spring is one of the most popular sights. The soft pink petals are an icon of the country. There is an unlimited choice of shopping, many museums that cover every era of Japanese art history, and even a robot restaurant.
- Kyoto is made of religious architecture, with around 2000 temples and shrines. It moves at a slower pace than any other city in Japan. Filled with samurais, geishas, Zen gardens, and the torii gate, Kyoto is the spiritual center of Japan. The city is also known for its food, head to the Nishiki Market, a four-hundred-year-old local food market that offers a range of national cuisine to modern food from all over the world.
- Osaka, the second largest metropolitan area after Tokyo is known to be the most delicious city. The city is nicknamed “the nation’s kitchen.” Visit Dotonburi to experience the food culture of Osaka. Besides the food, there are numerous attractions that tourists should visit such as Universal Studios Japan, Cup Noodles Museum, Aquarium Kaiyukan, Osaka Castle, and Umeda Sky Building.
- Fukuoka has a welcoming feel with sunny weather and so much to do. It’s made up of two towns, the port city of Hakata and the former castle town of Fukuoka. Visit the impressive Fukuoka Castle, explore the Sumiyoshi-Jinja Shrine, learn history in Kyūshū National Museum, experience the ancient art of calligraphy and origami in Hakata Machiya Folk Museum, and enjoy a calming bath in one of the Onsen hot springs.
- Nagoya is the industrial center of Japan. It’s the birthplace of Toyota and a popular pinball-style game Pachinko. Although many of the historic buildings were destroyed in the air raids of 1945, tourists can still indulge in its culture and tradition. Visit the Nagoya Castle that was reconstructed in 1959, walk around the Atsuta Shrine, or see the history of the automobile in the Toyota Automobile Museum.
Weather and Climate in Japan
Japan has four distinct seasons.
- Summer starts in June and lasts until August. The temperature can get very hot, up to 40 °C in some places, with high humidity. June is the rainy season where the farmers plant their rice. The rainy season is over in August but the typhoon season starts to peak.
- Autumn starts in September and ends in November. September has the greatest risk of typhoons. The weather is generally mild. October is pleasantly warm with less humidity than in summer, making it a food time for traveling the country.
- The temperature will drop in Winter. It lasts from December to February and is usually dry, pleasant, and sunny. The average temperature is around 2°C to 12°C, it rarely drops below 0°C. The northern island of Hokkaido, the Japan Alps, and the Japan Sea coast get a lot of snow while Tokyo gets very little snow.
- Spring is said to be the best time to visit Japan because of its mild weather and cherry blossoms. The season starts in March and ends in May. The temperature will gradually increase during spring with little rainfall and clear sky.
Getting Around in Japan
The main airport for international tourists is the Narita International Airport. It is located around 60km east of central Tokyo. It serves both domestic and international flights to almost every major city around the globe. There are several budget airlines that operate flights from this airport, namely Jetstar Japan, Eastar Jet, and Peach. There are other international airports such as Kansai International Airport, New Chitose International Airport, and Kyushu Saga International Airport.
To get to Tokyo from Narita Airport, tourists can use the rail, bus, taxi, or car rental. The most affordable train line is the Keisei Line that connects with the Toei Asakusa Subway Line and the Yamanote Line, it costs around ¥1,190 to ¥1,230 ($10 to $11.3). There’s also the Sky Access Express train that offers better access to Tokyo, a trip to Asakusa will cost around ¥1,290 ($11.9) and take about 58 minutes. The quickest way to get to Tokyo will be by the Skyliner train, it takes just 36 minutes to Nippori and will cost around ¥2,470 ($22.7). The airport introduced N’EX Tokyo Round-Trip ticket for foreign passport holders that provides round-trip travel from Narita to Tokyo and back for ¥4,000 ($37) for adults and ¥2,000 ($18.4) for children.
A regular taxi from Narita to Tokyo is very expensive, usually over ¥20,000 ($184). The best option is the shared minibus that starts with ¥6,180 ($57) per person. Buses are usually more affordable, the Limousine Bus costs ¥2,880 ($26.5) and the Tokyo Shuttle costs around ¥900 ($8) to ¥1,000 ($9).
Getting around Japan is fairly easy because the country has excellent public transportation. It is recommended to get a Japan Rail Pass. Japan’s bullet train is fast but expensive. There are cheaper train options. Buses are less expensive but will take more time than trains.
Tourist Visas in Japan
Citizens of 68 countries and territories can enter and stay in Japan for up to 90 days without a visa. Citizens of Indonesia, Brunei, and Thailand are granted a 15-day visa-free trip to Japan. Citizens of the United Arab Emirates are allowed to stay for 30 days without a visa. It is advisable to contact the nearest Consular Section of the Embassy or Consulate General of Japan for more information.
Additional Information
- Local Currency: Yen (¥) is the local currency. $1 will get you ¥11 ¥1,000 is worth approximately $9.
- Money & Payments: ATMs are usually located in post offices and convenient stores. There are only a few branches of major Japanese banks that accept foreign-issued cards. Credit cards are accepted in major cities, but the rural area doesn’t. It’s best to always bring cash and bring a coin purse because everything below ¥500 is coins. Tipping is not mandatory, high-end hotels and restaurants usually add a 10% service fee to the bill.
- Local Language: The official language is Japanese. English is common in major cities with many tourists such as Tokyo, Osaka, and Tokyo. Some restaurants write their menu in English and Japanese.
- Local Culture and Religion: The dominant religion in Japan is Shinto and Buddhism. There’s a small group of Christians as well.
- Public Holidays: Japan has sixteen national holidays each year, including Children’s Day, Constitution Memorial Day, and Marine Day. The country hosts numerous annual festivals such as Gion Matsuri in Kyoto, Awa Odori in Tokushima, and Yuki Matsuri Snow Festival in Sapporo.
Popular Searches
- Plastic Surgery in Thailand
- Dental Implants in Thailand
- Hair Transplant in Thailand
- Breast Augmentation Thailand
- Gastric Sleeve in Thailand
- Gender Reassignment Surgery in Thailand
- Laser Hair Removal in Bangkok
- Botox in Bangkok
- Dermatology in Bangkok
- Breast Augmentation in Bangkok
- Coolsculpting in Bangkok
- Veneers in Turkey
- Hair Transplant in Turkey
- Rhinoplasty in Turkey
- Stem Cell Therapy in Mexico
- Rhinoplasty in Mexico
- Liposuction in Mexico
- Coolsculpting in Tijuana
- Rhinoplasty in Korea
- Scar Removal in Korea
- Gastric Sleeve in Turkey
- Bone Marrow Transplant in India
- Invisalign in Malaysia
- Plastic Surgery in the Dominican Republic
- Tummy Tuck in the Dominican Republic
- Plastic and Cosmetic Surgery in Poland
- Rhinoplasty in Poland
- Hair Implant in Poland
- Dental Implants in Poland
- IVF in Turkey